アプリ関連ニュース
- 2021年11月25日
- Web Service
Cleaning Up Laravel Controllers
Introduction
Controllers play a huge role in any MVC (model view controller) based project. They’re effectively the “glue” that takes a user’s request, performs some type of logic, and then returns a response.
The Problem with Bloated Controllers
Bloated controllers can cause several problems for developers. They can:
1. Make it hard to track down a particular piece of code or functionality.
2. Make it difficult to spot the exact location of a bug.
3. Make it harder to write tests for more complex requests.
The Bloated Controller
For this blog, I am going to use an example UserController:
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function store(Request $request): RedirectResponse
{
$this->authorize('create', User::class); $request->validate([
'name' => 'string|required|max:50',
'email' => 'email|required|unique:users',
'password' => 'string|required|confirmed',
]); $user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => $request->password,
]); $user->generateAvatar();
$this->dispatch(RegisterUserToNewsletter::class); return redirect(route('users.index'));
} public function unsubscribe(User $user): RedirectResponse
{
$user->unsubscribeFromNewsletter(); return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
}
1. Lift Validation and Authorization into Form Requests
One of the first things that we can do with the controller is to lift any validation and authorization out of the controller and into a form request class.
We’ll use the following Artisan command to create a new form request:
php artisan make:request StoreUserRequest
The above command will have created a new app/Http/Requests/StoreUserRequest.php class that looks like this:
class StoreUserRequest extends FormRequest
{
/**
* Determine if the user is authorized to make this request.
*
* @return bool
*/
public function authorize()
{
return false;
}
/**
* Get the validation rules that apply to the request.
*
* @return array
*/
public function rules()
{
return [
//
];
}
}
We can use the authorize() method to determine if the user should be allowed to carry out the request. The method should return true if they can and false if they cannot. We can also use the rules() method to specify any validation rules that should be run on the request body.
class StoreUserRequest extends FormRequest
{
/**
* Determine if the user is authorized to make this request.
*
* @return bool
*/
public function authorize(): bool
{
return Gate::allows('create', User::class);
}
/**
* Get the validation rules that apply to the request.
*
* @return array
*/
public function rules(): array
{
return [
'name' => 'string|required|max:50',
'email' => 'email|required|unique:users',
'password' => 'string|required|confirmed',
];
}
}
Our controller should now also look like this:
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function store(StoreUserRequest $request): RedirectResponse
{
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => $request->password,
]);
$user->generateAvatar();
$this->dispatch(RegisterUserToNewsletter::class);
return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
public function unsubscribe(User $user): RedirectResponse
{
$user->unsubscribeFromNewsletter();
return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
}
2. Move Common Logic into Actions or Services
Another step that we could take to clean up the store() method could be to move out our "business logic" into a separate action or service class.
class StoreUserAction
{
public function execute(Request $request): void
{
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => $request->password,
]);
$user->generateAvatar();
$this->dispatch(RegisterUserToNewsletter::class);
}
}
Now we can update our controller to use the action:
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function store(StoreUserRequest $request, StoreUserAction $storeUserAction): RedirectResponse
{
$storeUserAction->execute($request);
return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
public function unsubscribe(User $user): RedirectResponse
{
$user->unsubscribeFromNewsletter();
return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
}
3. Use Resource or Single-use Controllers
A great way of keeping controllers clean is to ensure that they are either “ resource controllers” or “ single-use controllers”.
A resource controller is a controller that provides functionality based around a particular resource. So, in our case, our resource is the User model and we want to be able to perform all CRUD (create, update, update, delete) operations on this model. A resource controller typically contains index(), create(), store(), show(), edit(), update() and destroy() methods.
A single-use controller is a controller that only has one public __invoke() method. These are really useful if you have a controller that doesn't really fit into one of the RESTful methods that we have in our resource controllers.
So let’s create a new controller using the following Artisan command:
php artisan make:controller UnsubscribeUserController -i
Notice how we passed -i to the command so that the new controller will be an invokable, single-use controller. We should now have a controller that looks like this:
class UnsubscribeUserController extends Controller
{
public function __invoke(Request $request)
{
//
}
}
We can now move our method’s code over and delete the unsubscribe method from our old controller:
class UnsubscribeUserController extends Controller
{
public function __invoke(Request $request): RedirectResponse
{
$user->unsubscribeFromNewsletter();
return redirect(route('users.index'));
}
}
Conclusion
Hopefully this article has given you an insight into the different types of things you can do to clean up your controllers in your Laravel projects.
Tsuki
tsuki at 2021年11月25日 10:00:00
- 2021年11月24日
- 技術情報
Django & Laravel
Today I would like to share about advantages and disadvantages between Django and Laravel framework. First of all, as we know, each framework has each property and market. So this article just describes about the pros and cons.
What is Django?
Django is a web framework operating with Python programming language. Django is more suitable for implementing such technologies as AI(Artificial Intelligence) and ML(Machine Learning). Django follows the MVT(model view template) architectural pattern. It is adaptable to almost any project in various industries and includes various ready-made feature packages.
What is Laravel?
Laravel is a web framework that runs on PHP and maintains the MVC (model view controller) architectural pattern. It involves lots of additional libraries that make the development process more simple and supports the object-oriented approach. Laravel is supported by comprehensive documentation and detailed tutorials.
Advantages of Django
- is easily adjustable to any project;
- scalability;
- SEO tools included;
- quick prototype creating;
- generous dev community support and extensive documentation;
- easy data management
Disadvantages of Django
- Knowledge of full system is required to work
- creating API by yourself
- not very suitable for small projects
- Uses routing pattern specify its URL
Advantages of Laravel
- fast development
- clean and user-friendly architecture
- growing developer community
- a built-in command-line Artisan
- large cloud storage for files
- an easy way to build API
- ability to operate on numerous file systems simultaneously
Disadvantages of Laravel
- the syntax is difficult for beginners
- having to deal with standards
- no shared hosting support included
- unnecessary queries on databases
That is all for now. Hope you enjoy it.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2021年11月24日 10:00:00
- 2021年11月22日
- Web Service
Interesting APIs for your dummy data
Sometimes, we need dummy data to add in our projects before the production or you just want to create a fun project with some fun data. Today I will share some interesting data resources , also APIs you can try.
Movies API
The API service is intended for anyone interested in using images and data from movies, TV shows, and actors in their applications. Our API is a system provided by you and your team to acquire and use data and images programmatically.
API : API Overview — The Movie Database (TMDB) (themoviedb.org)
Meals API
The meal API allows you to access random food data and use it in your application. This API includes all meal categories including images, materials, videos, country of each meal and many other features.
API : TheMealDB.com
Jokes API
The random jokes API allows you to fetch random jokes data in an easy way using Fetch, Ajax XHR and etc.
API : icanhazdadjoke
Unsplash API
Unsplash is a website that hosts “beautiful and free images and photos that you can download and use for any project.” You can use that API to fetch photos from Unsplash. You can use the Unsplash API to create an application with a background that changes to a random image at different times of the day.
API : Unsplash Image API | Free HD Photo API
Marvel API
The Marvel Comics API gives developers access to information about Marvel’s vast comic library from anywhere.
API : Marvel Developer Portal
I am sure there are other interesting APIs around the world but that is all from me now. Enjoy the data.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2021年11月22日 10:00:00
- 2021年11月19日
- 技術情報
Let’s create flutter UI without wasting too much time!
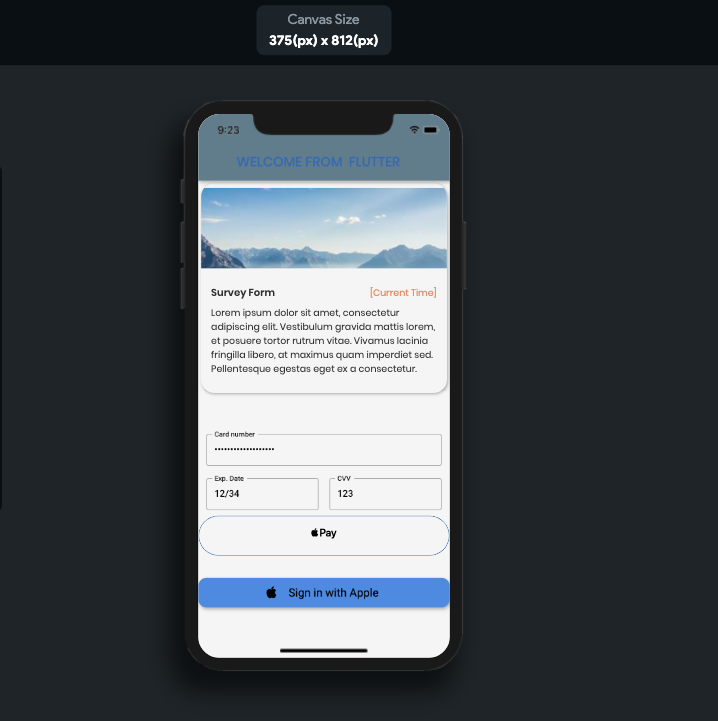
This time I would like to share about to create flutter design in mobile apps easily and quickly drag and drop. This name is flutter flow site that I found out.
Let’s take a look the site!
Firstly, we will create free account and after creation complete, we will see this page.
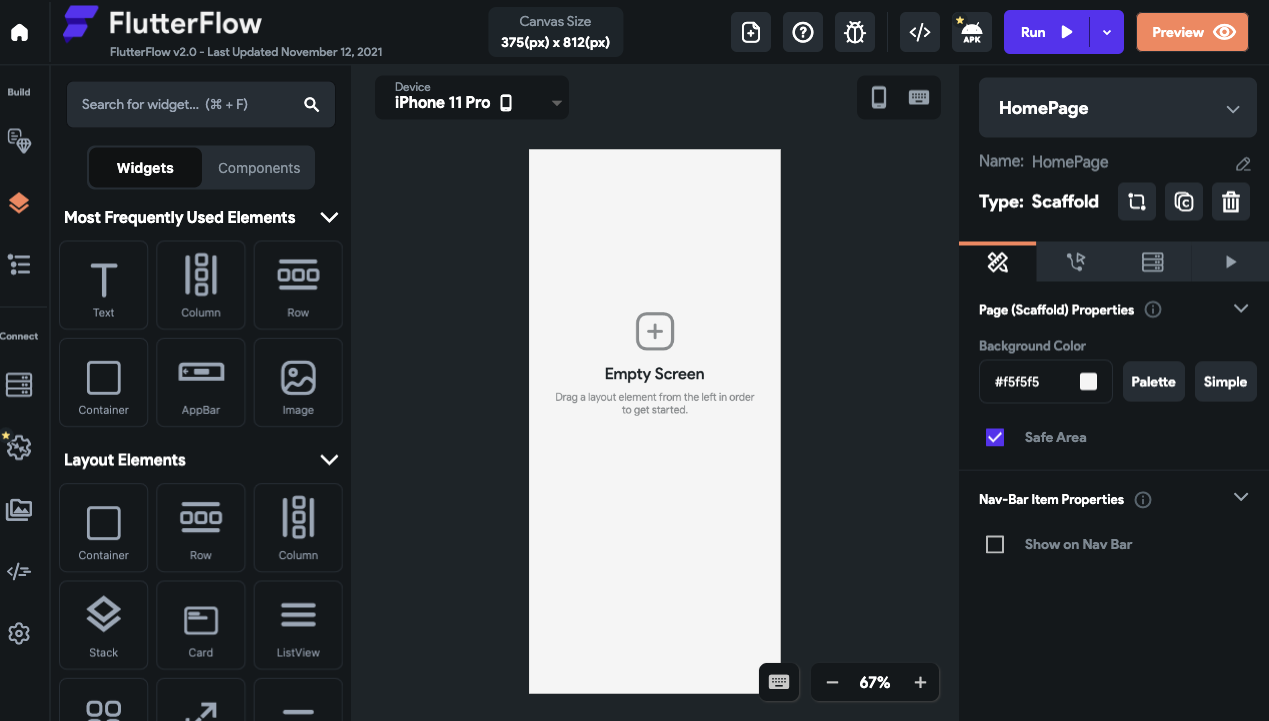
In the left side activity bar, we will see all of widgets, layouts, most popular form design etc. that you want to desire creation.
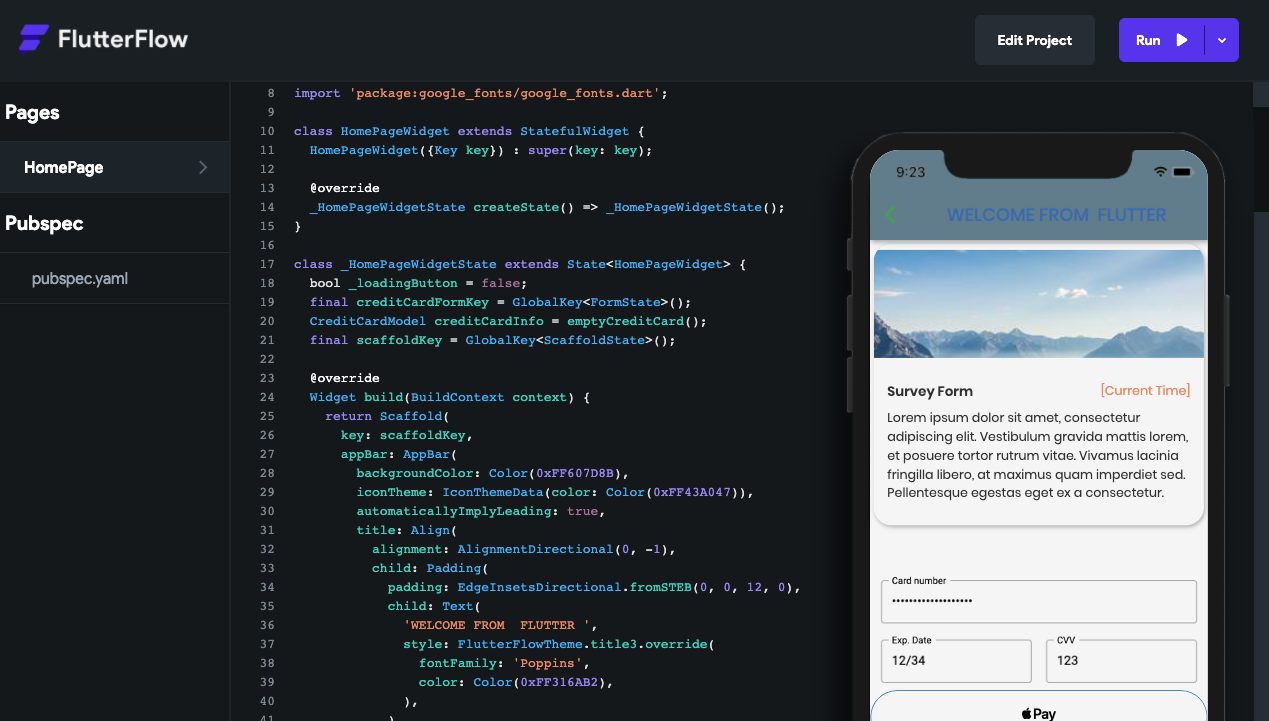
After running project or without running project, you can get your creation design code.And also if you want to get apk that also available. The below image is my creation of flutter code simple.
Hope you enjoyed my sharing article!
By Ami
asahi at 2021年11月19日 10:00:00
- 2021年11月18日
- 技術情報
LaravelでPDF出力処理を作成する
今回はLaravelでPDF出力をおこなうためのライブラリ「laravel-dompdf」の導入方法と
使用方法について紹介したいと思います。
必要なファイルのインストール
laravel-dompdf
https://github.com/barryvdh/laravel-dompdf
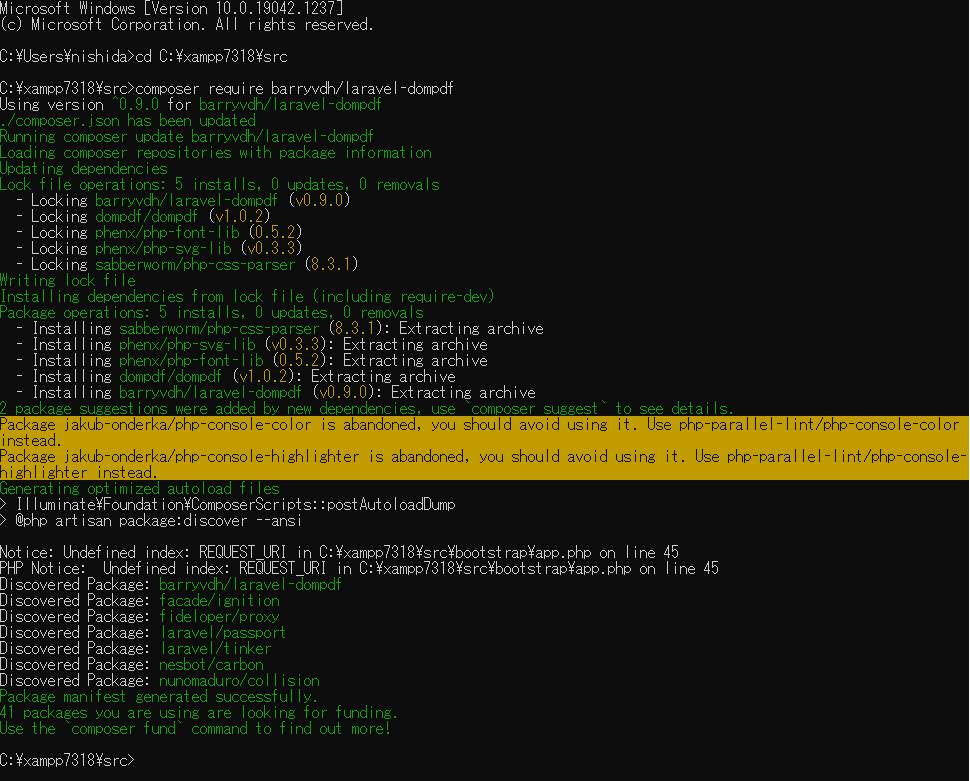
プロジェクトのルートディレクトリに移動をおこない
以下のコマンドを実行します。
composer require barryvdh/laravel-dompdf
※この操作をおこなうためにはcomposer 2のインストールが必要です。
コントローラー側の出力処理
PDFのレイアウトはbladeテンプレートのViewを作成するのと同じ要領でhtml/cssを使用して作成できます。
以下のようにテンプレートのViewを指定します。
$pdf = \PDF::loadView('pdf_template');
生成されたPDFをダウンロードさせるには以下の記述をおこないます。
以下の場合、ファイル名が「generated_pdf.pdf」のPDFファイルがダウンロードされます。
return $pdf->download('generated_pdf.pdf');
viewの準備
htmlのbladeテンプレートViewと同様に以下の階層にbladeテンプレートを作成します。\src\resources\views\pdf_template.blade.php
ページレイアウトはhtml/cssを使用して作成します。
PDFの改ページにはcssの page-break-after: always が使用できます。
<style>
hr {
page-break-after: always;
}
</style>PDFに日本語を表示する
標準の状態では日本語の表示に対応していませんので、
日本語用フォントを手動でインストールする必要があります。
今回はオープンソースの日本語フォント「IPAexフォント」を使用する方法を説明します。
IPAexフォントおよびIPAフォントについて
https://moji.or.jp/ipafont/
IPAexフォントは以下よりダウンロード可能です。
https://moji.or.jp/ipafont/ipafontdownload/
上記URLからダウンロードしたフォントファイル「ipag.ttf」を以下に配置します。
\src\storage\fonts\ipag.ttf
viewでは以下のように記述してフォント指定をおこないます。
<style>
@font-face {
font-family: ipag;
font-style: normal;
font-weight: normal;
src: url('{{ storage_path('fonts/ipag.ttf') }}') format('truetype');
}
@font-face {
font-family: ipag;
font-style: bold;
font-weight: bold;
src: url('{{ storage_path('fonts/ipag.ttf') }}') format('truetype');
}
</style>
木曜日担当:nishida
nishida at 2021年11月18日 10:00:00