アプリ関連ニュース
- 2021年12月17日
- 技術情報
Javascriptを使用して、Excelのセルにファイルアップロードを挿入する方法
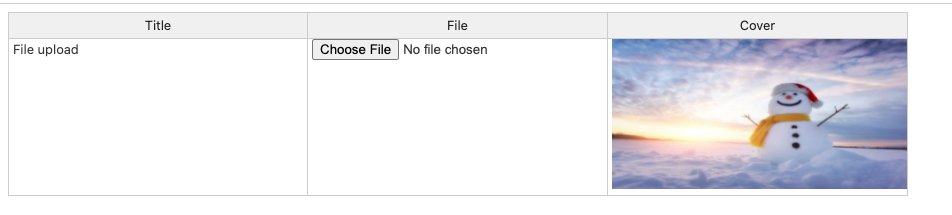
今回は、Handsontableを使って、ファイルアップロードボタンを挿入する方法と、セル内に画像を表示する方法を紹介したいと思います。
Handsontableは、デフォルトで11個のエイリアスを提供することができます。
- time
- text
- select
- password
- numeric
- handsontable
- dropdown
- date
- checkbox
- base
- autocomplete
しかし、file editorでは、これまで提供できませんでした。ファイルアップロードボタンをセルに挿入することは、自分自身で発見しました。4つの方法があるのですが、今日はそのうちの1つ、cells内で呼び出されるrenderer関数を使った方法を紹介します。
今回は、rendererの呼び出し方と、ファイルアップロードボタンと画像の表示方法を中心に説明します。
まず、htmlファイルを作成し、必要なスクリプトファイルを挿入します。
<div id="example1" class="hot "></div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/handsontable@11.0/dist/handsontable.full.min.js"></script>
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/handsontable@11.0/dist/handsontable.full.min.css" />
次に、Handontableを作成し、cells内にrendererを呼び出すための条件をいくつか作成します。commentsとcoversにcustom renderer関数を呼び出すことにします。
const hot = new Handsontable(container, {
data,
colWidths: [100, 100, 200],
colHeaders: ['Title', 'File', 'Cover'],
colWidths: 300,
renderer: 'html',
height: 200,
columns: [
{ data: 'title' },
{ data: 'comments', renderer: safeHtmlRenderer },
{ data: 'cover', renderer: coverRenderer }
],
cells: function (row, col, prop) {
var cellProperties = {};
if(col === 1){
cellProperties.renderer = safeHtmlRenderer
}
if(col === 2){
cellProperties.renderer = coverRenderer
}
},
licenseKey: 'non-commercial-and-evaluation'
});renderer関数の内部では、カスタムhtmlのデザインを作成し、innerHTMLプロパティでtdに挿入することができます。
function safeHtmlRenderer(instance, td, row, col, prop, value, cellProperties) {
Handsontable.renderers.TextRenderer.apply(this, arguments);
td.innerHTML = '<div><input type="file" id="filechange" name="file[]" class="filebutton"></div>';
return td;
}また、rendererで画像を表示することもできます。
function coverRenderer(instance, td, row, col, prop, value, cellProperties) {
Handsontable.renderers.TextRenderer.apply(this, arguments);
td.innerHTML = '<img src="imges/winter.jpg" width="300" height="150" >';
return td;
}ここまでお読みいただき、ありがとうございました。
By Ami
asahi at 2021年12月17日 10:00:00
- 2021年12月16日
- Web Service
Tips & best practices for Laravel 8
This article will show you the mysterious tricks that might help you when writing code with Laravel.
1.Use local scopes when you need to query things
Laravel has a nice way to write queries for your database driver using Query Builder. Something like this:
$orders = Order::where(‘status’, ‘delivered’)->where(‘paid’, true)->get();
This is pretty nice.But this bit of code can be better written if we use local scopes.
Local scopes allow us to create our Query Builder methods we can chain when we try to retrieve data. For example, instead of ->where() statements, we can use ->delivered() and ->paid() in a cleaner way.
First, in our Order model, we should add some methods:
class Order extends Model
{
...
public function scopeDelivered($query) {
return $query->where('status', 'delivered');
} public function scopePaid($query) {
return $query->where('paid', true);
}
}
When declaring local scopes, you should use the scope[Something] exact naming. In this way, Laravel will know that this is a scope and will make use of it in your Query Builder. Make sure you include the first argument that is automatically injected by Laravel and is the query builder instance.
$orders = Order::delivered()->paid()->get();
For more dynamic retrieval, you can use dynamic local scopes. Each scope allows you to give parameters.
class Order extends Model
{
...
public function scopeStatus($query, string $status) {
return $query->where('status', $status);
}
}$orders = Order::status('delivered')->paid()->get();
Laravel uses by default where[Something] to replace the previous scope. So instead of the previous one, you can do:
Order::whereStatus(‘delivered’)->paid()->get();
Laravel will search for the snake_case version of Something from where[Something]. If you have status in your DB, you will use the previous example. If you have shipping_status, you can use:
Order::whereShippingStatus(‘delivered’)->paid()->get();
2.Magic scopes
When building things, you can use the magic scopes that are already embedded
- Retrieve the results by
created_at, descending:
User::latest()->get();
- Retrieve the results by any field, descending:
User::latest('last_login_at')->get();
- Retrieve results in random order:
User::inRandomOrder()->get();
- Run a query method only if something’s true:
3.Do not store model-related static data in configs
Instead of this:
BettingOdds.php
class BettingOdds extends Model
{
...
}
config/bettingOdds.php
return [
'sports' => [
'soccer' => 'sport:1',
'tennis' => 'sport:2',
'basketball' => 'sport:3',
...
],
];
And accessing them using:
config(’bettingOdds.sports.soccer’);
I prefer doing this:
BettingOdds.php
class BettingOdds extends Model
{
protected static $sports = [
'soccer' => 'sport:1',
'tennis' => 'sport:2',
'basketball' => 'sport:3',
...
];
}
And access them using:
BettingOdds::$sports['soccer'];
Because it’s easier to be used in further operations:
class BettingOdds extends Model
{
protected static $sports = [
'soccer' => 'sport:1',
'tennis' => 'sport:2',
'basketball' => 'sport:3',
...
];public function scopeSport($query, string $sport)
{
if (! isset(self::$sports[$sport])) {
return $query;
}
return $query->where('sport_id', self::$sports[$sport]);
}
}
Now we can enjoy scopes:
BettingOdds::sport('soccer')->get();
4.Use collections instead of raw-array processing
Back in the days, we were used to working with arrays in a raw way:
$fruits = ['apple', 'pear', 'banana', 'strawberry'];foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
echo 'I have '. $fruit;
}
Now, we can use advanced methods that will help us process the data within arrays. We can filter, transform, iterate and modify data inside an array:
$fruits = collect($fruits);$fruits = $fruits->reject(function ($fruit) {
return $fruit === 'apple';
})->toArray();['pear', 'banana', 'strawberry']
Tsuki
tsuki at 2021年12月16日 10:00:00
- 2021年12月16日
- 技術情報, Web Service, スマホ
JavaScriptでQRコードをスキャンする
今回はJavaScriptでQRコードをスキャンするライブラリcozmo/jsQR(https://github.com/cozmo/jsQR)を紹介します。
前回の記事「PHP QRコード生成ライブラリ「endroid/qr-code」」ではQRコードの生成方法を紹介しましたが、今回は生成したQRコードをスマートフォンやPCのWebカメラを使用してJavaScriptでスキャンする方法を紹介いたします。
続きを読むnishida at 2021年12月16日 10:00:00
Windows上でAndroid向けゲームがプレイ可能に
GoogleがPC向けサービス Google Play Games を The Game Awards に合わせて発表しました。
2022年にPC上でAndroid向けゲームがプレイ可能になるとの事です。
公開された動画は The Game Awards のTwitterで見ることができます。
tanaka at 2021年12月15日 10:00:00
- 2021年12月14日
- 技術情報
Converting images into a pdf in python
Last weekend, my friend asked me to help him something about rearranging images and converting them into a pdf with only portrait view and sorting by modified date . But the images were not sorted by that and some in landscape. They were in chaos. Actually there are many online tools to do that. But most of them were not compatible with all what I wanted. Then I decided to do with a python program and wrote the following small code block. Let’s take a look.
I’ve used the image library called Pillow(PIL) and built-in module named os.
Overall program flow is as follow.
- Request user inputs for a pdf filename with path and image folder path to be converted.
- With os module, image files are sorted by modified date.
- Looping the sorted files, rotate the images which are in landscape, to be in portrait with the help of Pillow(PIL) and push the images into an empty list named img_list[ ].
- Finally convert the images list to a pdf.
from PIL import Image
import os
# Function to sort by modified dates
def getfiles(dirpath):
a = [s for s in os.listdir(dirpath)
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dirpath, s))]
a.sort(key=lambda s: os.path.getmtime(os.path.join(dirpath, s)))
return a
# declare an empty list
img_list = []
# Request user input for pdf filename and image folder path
pdf_filename = input("Enter the filename of pdfincluding path to be exported : ")
folder = input("Enter the path of images folder : ")
files = getfiles(folder) # get the files sorted by modified dates
print('Processing....')
for count, filename in enumerate(files):
image = Image.open(folder+'/'+filename) #open each file
# To change as portrait layout for landscape images
width, height = image.size
if(width>height):
image = image.transpose(Image.ROTATE_90)
# Append each processed image in img_list[]
img_list.append(image)
# All images in img_list[] are converted to a pdf
img_list[0].save(pdf_filename, "PDF" ,resolution=100.0, save_all=True, append_images=img_list[1:])
print("Done!")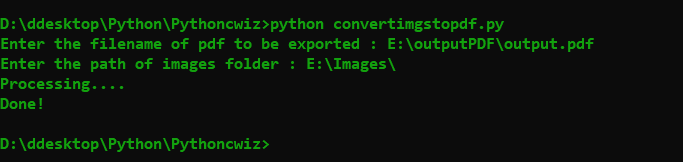
This program is very simple but it can be modified to be more useful for other cases. I hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2021年12月14日 10:00:00