アプリ関連ニュース
AndroidアプリのViewをPDFファイルとして出力する方法
tanaka at 2023年06月21日 10:00:00
- 2023年6月19日
- 技術情報
Mercedes is assembling ChatGPT to their vehicles
US based company Mercedes will soon be adding ChatGPT to their luxury cars. The automaker is adding an OpenAI conversational AI agent to his MBUX infotainment system, but the reason is quite unknown.
US owners of models that use MBUX will be able to opt-in to the beta program starting from June 16th, by activating the ChatGPT feature. This allows a versatile large-scale language model to improve the vehicle’s ability to speak. All you have to do is look at your car and say, “Hello Mercedes, I would like to join the beta program.”
However, it is not very clear what it is for. After all, a car is a fairly limited environment. People need to drive, navigate, and control media and basic vehicle functions, and voice interfaces may be the safest or best option to do so without taking your eyes off the road.
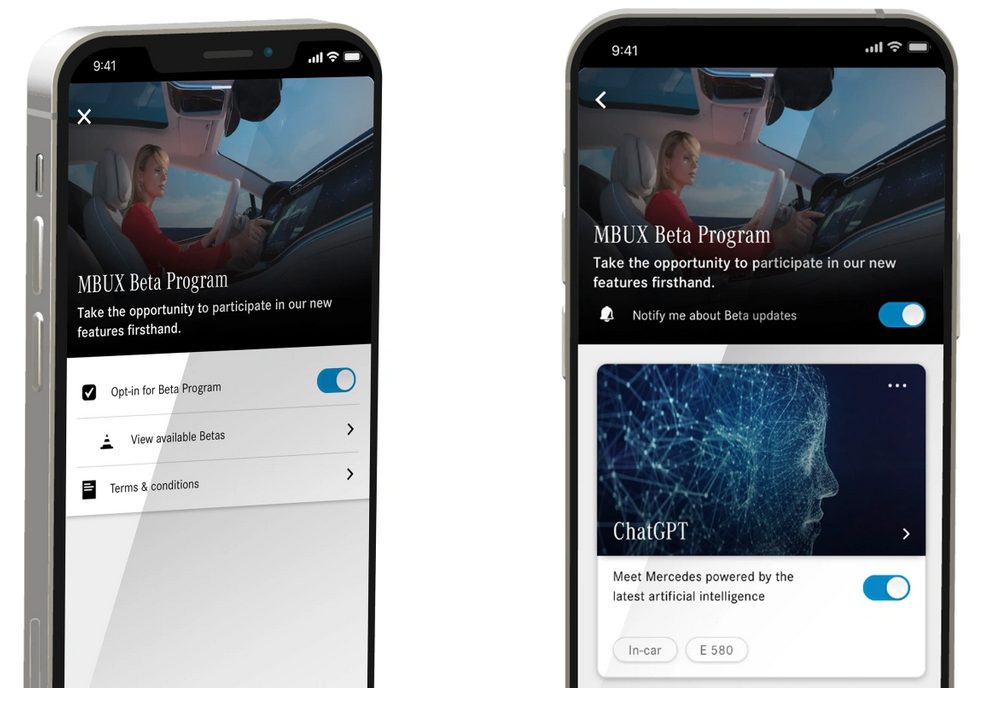
Mercedes said
Users will experience a voice assistant that not only accepts natural voice commands but can also conduct conversations. Soon, participants who ask the Voice Assistant for details about their destination, to suggest a new dinner recipe, or to answer a complex question, will receive a more comprehensive answer – while keeping their hands on the wheel and eyes on the road.
They also mentioned the data privacy as below.
A collaboration with Microsoft enables the integration of ChatGPT. Through Azure OpenAI Service, Mercedes‑Benz is tapping OpenAI’s large-scale generative AI models combined with the enterprise-grade security, privacy and reliability capabilities of Azure. Mercedes-Benz retains complete control over the IT processes in the background. The voice command data collected is stored in the Mercedes-Benz Intelligent Cloud, where it is anonymised and analysed.
You can take a look about the original article from Mercedes here.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2023年06月19日 10:00:00
- 2023年6月15日
- AI
OpenAI GPT API(6) プロンプトデザイン
nishida at 2023年06月15日 10:00:00
- 2023年6月14日
- AI
音楽生成AIをMeta社が公開
tanaka at 2023年06月14日 10:00:00
- 2023年6月13日
- 技術情報
Python Decorators
Today, I would like to share about Python decorators which simplify the code with powerful function enhancements. Python decorators are a powerful feature that allows developers to modify or enhance the behavior of functions or classes without directly modifying their source code. Decorators provide a clean and concise way to add functionality to existing code, making it easier to manage and reuse.
What are Decorators?
Decorators are functions that take another function as input and extend its functionality. They wrap the original function with additional code, allowing for actions like logging, authentication, and more, to be applied to multiple functions in a consistent and reusable manner.
Example 1: Logging Decorator
Let’s consider a simple example of a logging decorator. The decorator adds logging statements before and after the execution of a function:
def logger(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(f"Calling function: {func.__name__}")
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
print(f"Function {func.__name__} executed")
return result
return wrapper
@logger
def add(a, b):
return a + b
# Using the decorated function
result = add(3, 5)
print(result) # Output: 8In this example, the `logger` function is a decorator that takes the function `add` as input. It defines an inner function `wrapper`, which performs the logging operations and calls the original function. The decorator then returns the `wrapper` function, which replaces the original `add` function.
Example 2: Authorization Decorator
Decorators can also be used for implementing authorization checks. Let’s see an example:
def authenticate(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if check_authentication():
return func(*args, **kwargs)
else:
raise Exception("Unauthorized access!")
return wrapper
@authenticate
def sensitive_operation():
# Perform sensitive operation here
pass
# Using the decorated function
sensitive_operation()In this example, the `authenticate` decorator checks if the user is authenticated before executing the `sensitive_operation` function. If the user is authenticated, the function is executed; otherwise, an exception is raised.
Conclusion
Python decorators provide a powerful and flexible way to modify the behavior of functions or classes without modifying their original code. They enable code reuse, separation of concerns, and cleaner code organization. By using decorators, developers can enhance their programs with additional features, such as logging, authentication, caching, and more, with minimal effort and maximum efficiency.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2023年06月13日 10:00:00