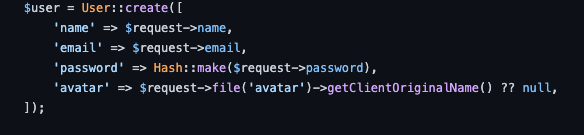
技術情報
- 2022年03月11日
- 技術情報
Laravel 8のメール送信の例と、alwaysTo()を使って誤送信を防ぐ方法
今回は、Laravel 8のメール送信の例と、alwaysTo()を使って誤送信を防ぐ方法を紹介します。
Laravel 8には、メール送信のためのmailクラスがあり、メール送信のためのドライバーを複数用意し、お好みで使用することができます。smtp、Mailgun、Postmark、Amazon SES、sendmailが使用できます。どのドライバを使用するかは、envファイルで設定する必要があります。
今回はsmtpドライバを使用します。
.envでSMTPを設定する
MAIL_MAILER=smtp
MAIL_HOST=smtp.gmail.com
MAIL_PORT=587
MAIL_USERNAME=Add your user name here
MAIL_PASSWORD=Add your password here
MAIL_ENCRYPTION=tls
MAIL_FROM_ADDRESS=Add your user name here※メールを使い場合、googleアカウントのless secure app accessでturnをオンにする必要があります。
利用可能なメールクラスの作成
以下のコマンドを使用して、MyTestMailという名でメイラブルクラスを作成します。
php artisan make:mail MyTestMailMyTestMailで以下のように変更する必要があり
public $details;
public function __construct($details)
{
$this->details = $details;
}
public function build()
{
return $this->subject('Mail from AMI')
->view('emails.myTestMail');
}ブレードビューの作成
ブレードビューファイルを作成し、送信するメールを記述します。「emails」フォルダに以下のようなファイルを作成します。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>メール送信テスト</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{ $details['title'] }}</h1>
<p>{{ $details['body'] }}</p>
<p>Thank you</p>
</body>
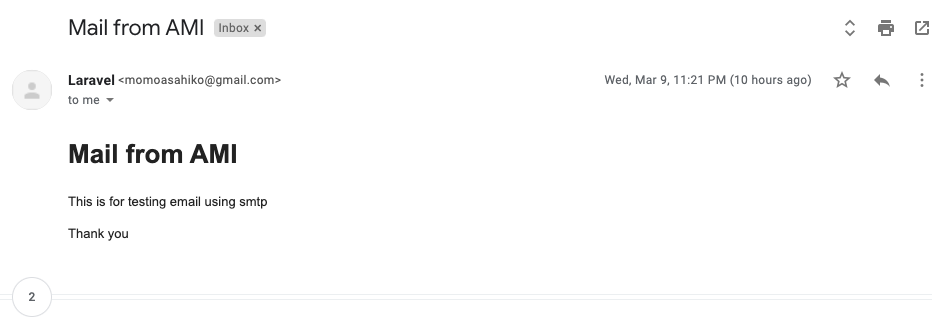
</html>最後に、テストメールを送信するための “MyTestMail “を作成します。
Route::get('send-mail', function () {
$details = [
'title' => 'Mail from AMI',
'body' => 'This is for testing email using smtp'
];
\Mail::to('name@gmail.com')->send(new \App\Mail\MyTestMail($details));
dd("Email is Sent.");
});プロジェクトを実行すると結果は
ステージング環境から実際のお客様に誤って何千通ものメールを送信してしまうこともあります。その時、どうのように設定するのかを共有します。
class AppServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
// Stuff omitted
public function boot()
{
f (! app()->environment('production')) {
Mail::alwaysTo('ex@example.org');
}
}
}alwaysToで何が起きているのか?
alwaysTo() メソッドは、メールメッセージ内の to, cc, bcc に追加されたすべてのアドレスを上書きします。
そこで、上記のコードでは、Laravelに、本番環境でない場合のみ、ex@example.org にメールを送信するように指示しています。
ということで今回はこれで終わりです。
By Ami
asahi at 2022年03月11日 10:00:00
- 2022年03月08日
- 技術情報
Useful Features of Rsync Command in Linux
Today, I would like to share about usefulness of rsync command in Linux and how to back up data with cron job. Let’s take a look.
Rsync (Remote Sync) is the most commonly used command for copying and synchronizing files and directories remotely as well as locally in Linux/Unix systems. Data can be copied, synchronized and backup both remotely and locally across directories, disks & networks.
Advantages of Rsync Command
- It efficiently copies and sync files from source to destination remotely or locally.
- It supports copying links, devices, owners, groups and permissions.
- rsync allows to transfer just the differences between source and destination. The first time, it copies the whole content of a file or a directory from source to destination but from next time, it copies only the changed files/data to the destination.
- Due to using compression and decompression method while transferring data, rsync consumes less bandwidth.
Installing Rsync
rsync is preinstalled on most Linux distributions and mac-OS. If rsync hasn’t been installed on the system, it can be installed easily using your distribution’s package manager as follows.
$ sudo apt-get install rsync [On Debian/Ubuntu & Mint]
$ pacman -S rsync [On Arch Linux]
$ emerge sys-apps/rsync [On Gentoo]
$ sudo dnf install rsync [On Fedora/CentOS/RHEL and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux]
$ sudo zypper install rsync [On openSUSE]
Rsync Basic Command Syntax
Local to Local
rsync [OPTION] [SRC] [DEST]
Local to Remote
rsync [OPTION] [SRC] [USER@]HOST:DEST
Remote to Local
rsync [OPTION] [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST]
Common options[OPTION] used with rsync commands
-v : verbose
-r : copies data recursively (but don’t preserve timestamps and permission while transferring data.
-a : archive mode, which allows copying files recursively and it also preserves symbolic links, file permissions, user & group ownerships, and timestamps.
-z : compress file data.
-h : human-readable, output numbers in a human-readable format.
For more options, the following command can be used.
$ rsync -h
For example, to backup data from local to local(external hard drive), the following command is commonly used.
rsync -azv /home/username/projects /media/username/SPHardDrive/BackupFolder
Schedule backups
To enable scheduled backups, cron can be used for the rsync commands.
Conclusion
This is all how to copy, synchronize and backup files & directories. And I recommend the link to learn more about rsync.
Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2022年03月08日 10:00:00
- 2022年03月04日
- 技術情報
Laravelのファイルアップロード: 重複するファイル名 – 解決するための2つの方法
今日は、ファイルのアップロードについて、特に、同じファイル名でファイルをアップロードできるようにするとどうなるか、古いファイル名を上書きしてしまうか、それをいろいろとお話したいと思います。
例えば、デフォルトで登録フォームがあり、アバターがあり、誰かがavator.jpgというファイル名でファイルをアップロードしたとします。これは正常にアップロードされているのですが、開発者がよくやるのは、ClientOriginalNameが悪意のないものであることを信じてファイル名をアップロードすることです。
しかし、元のファイル名を保持したい場合は、それは大丈夫かもしれません。しかし、同じファイル名で登録した人がいて、そのファイルがstorage/app/public/avatorsにavator.jpgとしてアップロードされた場合、問題が発生することがあります。
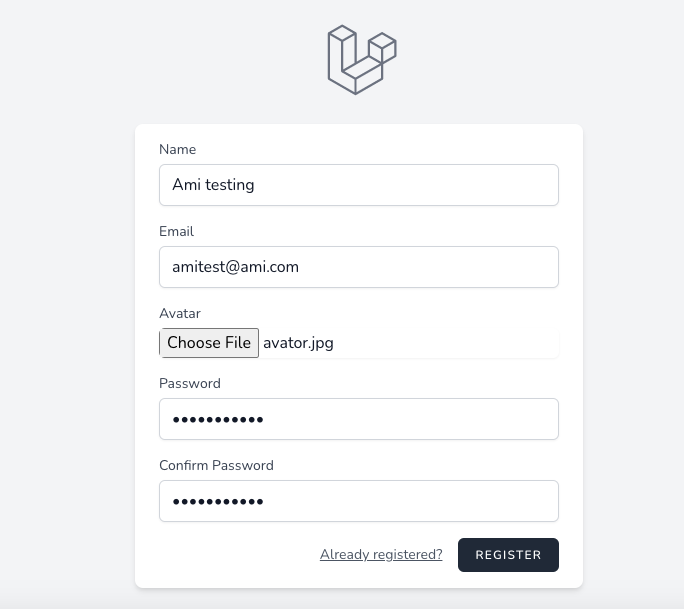
そして、別のユーザーで登録しようとし、ユーザー情報を入力し、異なるパスからアバターをアップロードしますが、ファイル名は同じです。登録後、古いアバターはやみくもに上書きされ、サーバーから削除されることさえあります。というわけで、これは今問題になっています。どのようにコードでそれを解決するかは、いくつかの異なる方法があります。
ということで、今からこの方法をお話ししたいと思います。
1つ目はファイル名を変更する方法です。
if ($request->file('avatar')) {
$fileName = pathinfo($request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalName(), PATHINFO_FILENAME) . '-' . $user->id . '.' . $request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalExtension();
$request->file('avatar')->storePubliclyAs('avatars', $fileName, 'public');
$user->update([
'avatar' => $fileName ?? null,
]);
}アベータがある場合、拡張子なしのファイル名からファイルを作成し、ユーザ登録からuser_id、そしてオリジナルの拡張子からファイルを構築することになります。そして、そのファイルをファイル名と一緒にパブリックドライバに保存し、ユーザを更新します。
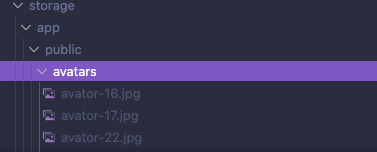
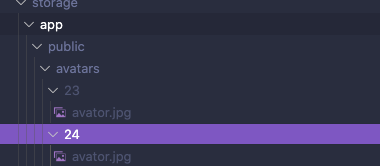
2つ目はサブフォルダを作成する方法です。
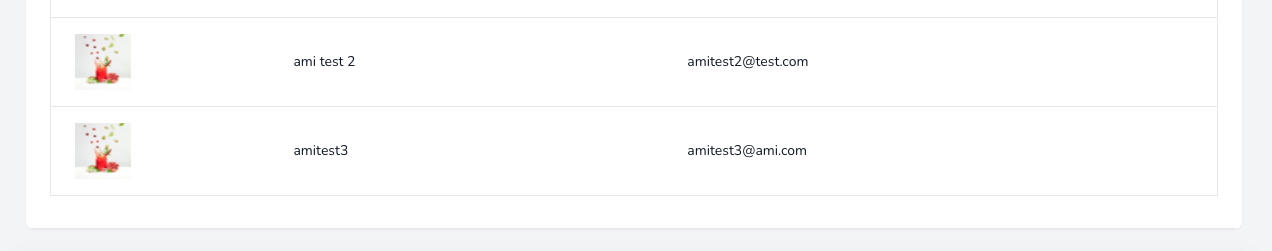
$request->file('avatar')->storePubliclyAs("avatars/{$user->id}", $request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalName(), 'public');publicのuser_idサブフォルダに元のファイル名で保存します。
結果一覧
はい。ということで今回は以上になります。
By Ami
asahi at 2022年03月04日 10:00:00
- 2022年03月03日
- 技術情報
DataTablesを使用したテーブル生成とサーバーサイド連携(4)
今回はDataTablesを使用したテーブル生成方法とサーバーサイド連携方法の連載Part4です。
前回の記事「DataTablesを使用したテーブル生成とサーバーサイド連携(3)」で発生した問題の原因と解決の方法について紹介いたします。
nishida at 2022年03月03日 10:00:00
- 2022年03月01日
- 技術情報
Comparisons between Ubuntu and Linux Mint
Today, I would like to share about comparisons between Ubuntu and Linux Mint Operating systems. Let’s take a look.
Ubuntu is the most famous Linux distribution. Its development started back in 2004. It is based on Debian distribution, which is why Ubuntu also uses the dpkg packaging system (And .deb package format) along with the apt packager manager.
Linux Mint, on the other hand, is based on Ubuntu. Its development started in 2008. Hence, Mint by extension is also based on Debian, and uses the same package manager and packaging system.
1. Distribution Goals
Ubuntu does not aim to be a simple Linux desktop distribution. Instead, Ubuntu is a general-purpose Linux distribution that can be used on servers, cloud, IoT and embedded devices.
Linux Mint, on the other hand, is nothing more than a desktop Linux distribution. There are no Linux Mint versions for servers or cloud or IoT… etc.
2. Software Manager
Ubuntu Software Center is slow while interacting with it. Of course, things have improved over the years but even with Ubuntu 20.04, on board, you will often notice it loading up slow or freezing when updating/installing an app. On the other hand, Linux Mint’s Software Manager is lighter and quicker.
3. User Interfaces
Ubuntu comes with the GNOME desktop environment. GNOME is an open-source desktop environment, which means that it’s a collection of programs associated with a GUI. The GNOME GUI has a dock on the left side where you can see all opened applications.
Mint comes with Cinnamon as a default desktop environment. Cinnamon is a Windows-like interface with a launcher, panel, and a system notification area on the bottom.
Ubuntu does support other desktop environments like Budgie, KDE, and Xfce. Mint only supports KDE and Xfce in addition to its default, Cinnamon.
4. Memory Usage
Desktop environments usually consume a lot of memory in order to run, which reduces the performance of the OS. Both Cinnamon and GNOME have their own perks but Cinnamon consumes significantly lesser memory than Ubuntu Desktop, making Mint the best distro for old PCs. So, the advantage of Mint is Cinnamon’s lower memory consumption as compared to GNOME.
5. Preinstalled Applications
Every Linux distribution comes with preinstalled applications like internet browsers, video players, image editors, and text editors. While Ubuntu offers more applications, their applications are difficult to search for, as you have to remember the exact name of the application. You can’t just guess the name or depend on browsing to find it.
Mint, on the other hand, only offers basic applications, but those applications are easy to find on their Windows-like menu.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2022年03月01日 10:00:00