アプリ関連ニュース
- 2022年1月18日
- 技術情報
4 mistakes that should be careful in NodeJS
Today, I would like to share about four common mistakes that should be careful when develop with NodeJS. Let’s take a look.
Blocking the Event Loop
Since Node JS comes with a single-threaded environment, no two parts of a Node JS application can run parallelly.
So, If the event loop is blocked, it causes blocking everything.
The solution is to use open-source modules like StrongOps.
StrongOps can identify and fix any delays in the event loop and prevent from blocking the event loop.
Trying to Execute Multiple Callbacks
Callbacks is used to allow asynchronous elements to communicate with each other.
However, executing the same callbacks or multiple callbacks all at once can cause interface freeze.
Therefore, it’s important to ensure you’re not continuously pressing for callbacks multiple times.
There are two ways to avoid that.
First, you can wrap the callback so you’ll be notified each time a callback is executed twice.
The second solution is to add a return before the callback to prevent invoking the same callback more than once.
Callback Hell
Callback Hell means multiple nested callbacks that make nesting callbacks difficult and impossible to read & debug the written code.
There are many ways to keep the code easy-to-read and debug such as using promises.
A promise is basically a value returned to confirm the processing done by an asynchronous function. In simple terms, promises can be nested to make complex code look clear and easier to maintain.
Another way is to use the async module that provides a straight forward, powerful functions to work with asynchronous JavaScript.
Using Console.log for Debugging
Console.log in the NodeJS is to print almost anything to the console. When Console.log is used to debug, it restarts the server and slows down the performance of the application.
We can’t use console.log every time. So instead of console.log, we can use the Debug Library.
This is all for now.
Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2022年01月18日 10:00:00
- 2022年1月17日
- 技術情報
Demanding Technologies for developers in 2022
Regardless of your profession or designation, you must adapt to the constant changes that occur in your workplace. You need to learn new work skills through your work to adapt to changes in the workplace, develop your career, and promote career opportunities.
There might be plenty of trending and demanding technologies for 2022. I will describe a few which are demanding and also depending on my personal favors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence experts focus on building machines that are programmed to think like humans. These machines can perform tasks that require human intelligence. It exists a variety of actions related to human intelligence, such as knowledge representation, problem solving, learning, and reasoning.
AI has become so popular lately. The demand for professionals with knowledge, experience and skills in AI is very high. It goes without saying that careers in the field of AI have potential and are expected to continue in the future.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions that is replicated and distributed thousands of times through a network of computer systems on the blockchain. This is the process of recording information in a way that makes system changes and hacks difficult or impossible.
Given the market trends, the demand for blockchain professionals continues to grow. If you have all the important blockchain-related tools and knowledge, you certainly have a brilliant career.
DevOps
A set of practices and tools that combine software development and IT operations to shorten the system development life cycle. Simply put, its goal is to make the software creation, testing, and launch process faster and more reliable.
DevOps experts are dedicated to creating software and verifying code versions to make sure everything goes smoothly. This is one of the most expensive remote jobs on the market.
AR & VR
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are technologies that connect the real and virtual worlds. These technologies provide users with a visual view of information and content as if it were in the world. Many industries such as healthcare, travel, aviation and automotive are developing augmented reality solutions in training applications.
AR adds digital elements to live views to enhance the usefulness of digital devices in everyday tasks such as information retrieval and shopping. Virtual reality, on the other hand, allows users to experience what it is like to go anywhere.
While augmented reality provides an interactive experience of real-world scenarios, virtual reality creates a fully immersive virtual environment.
There are still other demanding techs like I said in above such as cyber security, robotics, machine learning etc. Wish everyone may be healthy and have a productive year.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2022年01月17日 10:15:00
- 2022年1月14日
- 技術情報
Laravel8でFullcalendarとAJAXを使ってイベントを作成する
今週は、Laravel 8アプリにFullcalendar JavaScriptイベントカレンダープラグインを使用してイベントを作成・削除する方法を紹介します。
今回はプロジェクトのセットアップをスキップします。
プロジェクトの設定後、イベントの作成、削除を行うために、新しいカレンダーを作成する必要があります。そのために
php artisan make:controller FullCalenderControllerそして、app\Http\Controllersの中の、FullCalenderController.phpで、FullcalendarイベントのビューとCDオペレーションを設定することになります。
public function index(Request $request)
{
if($request->ajax()) {
$data = Event::whereDate('start', '>=', $request->start)
->whereDate('end', '<=', $request->end)
->get(['id', 'title', 'start', 'end']);
return response()->json($data);
}
return view('welcome');
}この関数は、作成したイベントが表示されていることを取得します。public function calendarEvents(Request $request)
{
switch ($request->type) {
case 'create':
$event = CrudEvents::create([
'event_name' => $request->event_name,
'event_start' => $request->event_start,
'event_end' => $request->event_end,
]);
return response()->json($event);
break;
case 'delete':
$event = CrudEvents::find($request->id)->delete();
return response()->json($event);
break;
default:
# ...
break;
}
}リクエストタイプはcreateで、create caseを入力すると、イベントが作成され、json形式で返されます。
リクエストタイプはdeleteで、delete caseを入力すると、作成されたイベントを削除して、json形式で返されます。
Controllerがセットアップされたので、次は routes/web.php ファイルに移動します。このファイルでは、ルートを作成するために FullCalenderControllerを使用する必要があります。
Route::get('calendar-event', [FullCalenderController::class, 'index']);
Route::post('calendar-crud-ajax', [FullCalenderController::class, 'calendarEvents']);最後に、laravel bladeのビューファイルでフFull calenderを表示し、jQueryのAJAXリクエストでイベントの作成、削除を行う必要があります。
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.1.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/moment.js/2.29.1/moment.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/fullcalendar/3.10.2/fullcalendar.min.js"></script>
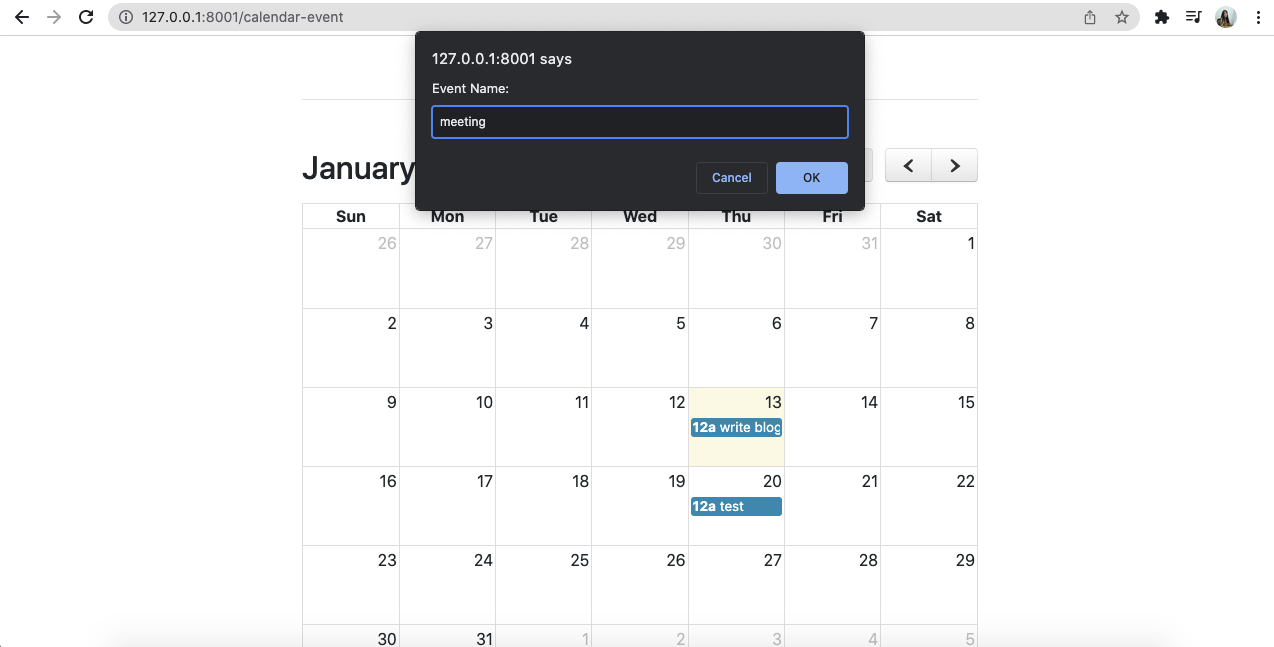
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/toastr.js/latest/toastr.min.js"></script>カレンダーの日をクリックすると、入力タイプのフィールドが表示され、OKボタンをクリックすると、ajaxリクエストでコントローラに移動し、ajaxリクエストで戻り、イベントが作成されます。
また、作成したイベントをクリックすると、アラートボックスが表示され、OKボタンをクリックすると、作成したイベントが削除されます。
この状態に対して
$(document).ready(function () {
var SITEURL = "{{ url('/') }}";
$.ajaxSetup({
headers: {
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content')
}
});
var calendar = $('#full_calendar_events').fullCalendar({
editable: true,
editable: true,
events: SITEURL + "/calendar-event",
displayEventTime: true,
eventRender: function (event, element, view) {
if (event.allDay === 'true') {
event.allDay = true;
} else {
event.allDay = false;
}
},
selectable: true,
selectHelper: true,
select: function (event_start, event_end, allDay) {
var event_name = prompt('Event Name:');
if (event_name) {
var event_start = $.fullCalendar.formatDate(event_start, "Y-MM-DD HH:mm:ss");
var event_end = $.fullCalendar.formatDate(event_end, "Y-MM-DD HH:mm:ss");
$.ajax({
url: SITEURL + "/calendar-crud-ajax",
data: {
event_name: event_name,
event_start: event_start,
event_end: event_end,
type: 'create'
},
type: "POST",
success: function (data) {
displayMessage("Event created.");
calendar.fullCalendar('renderEvent', {
id: data.id,
title: event_name,
start: event_start,
end: event_end,
allDay: allDay
}, true);
calendar.fullCalendar('unselect');
}
});
}
},
eventClick: function (event) {
var eventDelete = confirm("Are you sure?");
if (eventDelete) {
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: SITEURL + '/calendar-crud-ajax',
data: {
id: event.id,
type: 'delete'
},
success: function (response) {
calendar.fullCalendar('removeEvents', event.id);
displayMessage("Event removed");
}
});
}
}
});
});
function displayMessage(message) {
toastr.success(message, 'Event');
}
</script>開発サーバーの実行
php artisan serve結果は上部に表示されます。
最後までお読みいただき、ありがとうございました。
By Ami
asahi at 2022年01月14日 10:00:00
- 2022年1月13日
- Web Service
ES9 Features
EcmaScript is the “official” name for JavaScript. It was eventually abandoned and ES3.1 became ES5, which is the JavaScript version used in the “HTML5” world. ECMAScript is the “standard for” the JavaScript language.
ECMAScript2018 or ES9 has been evolving for the last few years and it has improved a lot.
The top features of the ES9 are
1.Object Rest/Spread Properties
If you want to extract an object excluding one or more properties, you can do it in ES9. It was not possible in the previous versions.
Here is an example:
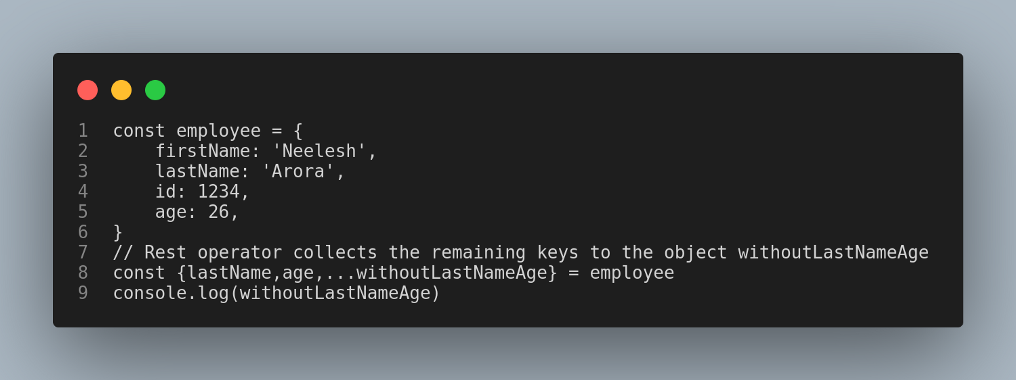
Output is

2.Regular Expressions (RegExp) named Groups
A capture group can be given a name using the (?<name>...) syntax. The groups can be accessed via the ‘groups’ property of the regular expression’s result. Numbered references to groups are also created as usual.
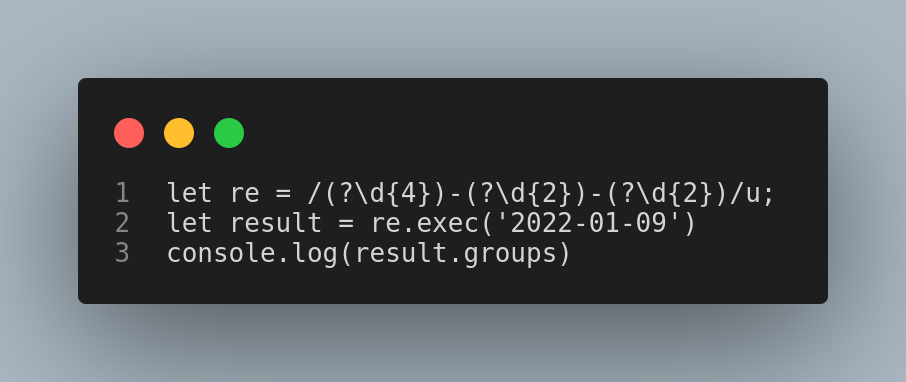
Output is :

3.Asynchronous Iterators
ES9 introduces the AsyncIterator interface, an asynchronous iteration statement (for — await — of), and async generator functions. The for — await — of statement creates a loop iterating over async iterable objects as well as on sync iterables. The loop can only be used in an async function.
Syntax:
for await (const variable of iterable) {
statement
}
4. Promise.prototype.finally
Promises now include a ‘finally’ method. You can use this when you want to perform an action irrespective of the promise being fulfilled or rejected. A good example of this would be turning off a loader after an API call is completed.
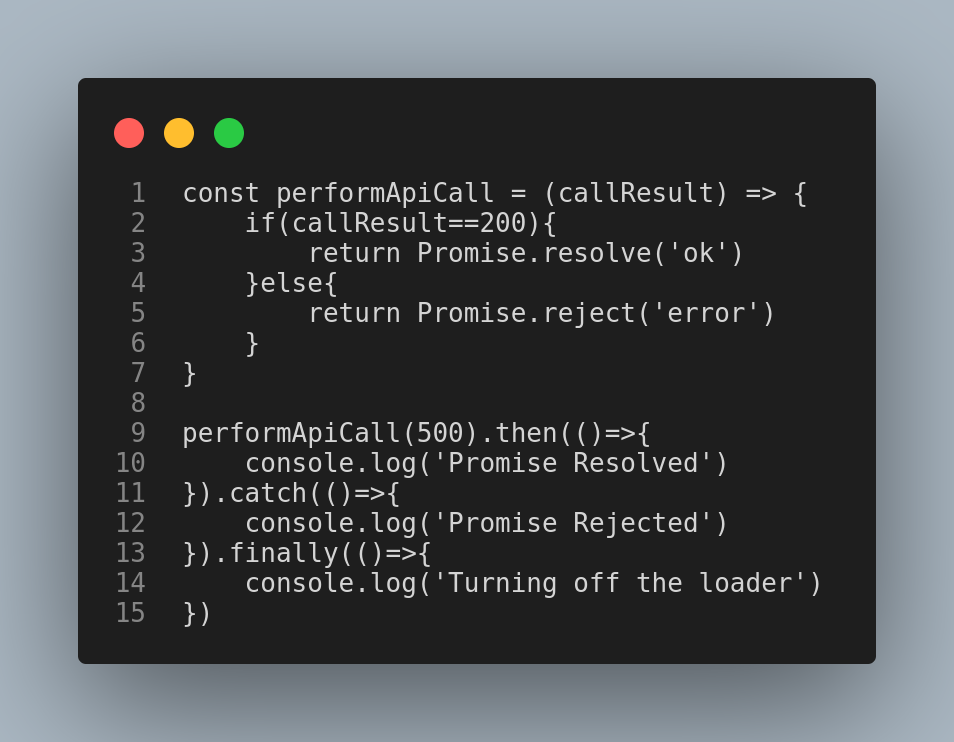
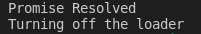
Output when 200 is passed.

Output when 500 is passed.
These were the features of ES9 that will definitely help to code in a better way.
Tsuki
tsuki at 2022年01月13日 10:00:00
- 2022年1月07日
- 技術情報
JetStreamを使用してLaravel 8 Livewire CRUDアプリケーションの作成
今回は、Laravelアプリケーションに必要不可欠なCRUD操作を、LivewireとJetstreamのパッケージを使って簡単に作成する方法を紹介します。
プロジェクトの設定
新しいlaravelアプリをインストールするので、ターミナルに向かい、コマンドを入力し、新しいlaravelアプリを作成します。
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel_livewire_crud.envでデータベースの詳細を追加する

Modelファイル、Migrationファイルの作成
php artisan make:model Student -m例え:
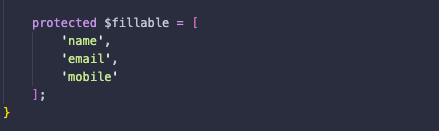
app/Models/Student.phpファイルに$fillable配列を追加し、名前、メール、携帯電話などのテーブルの値を追加します。
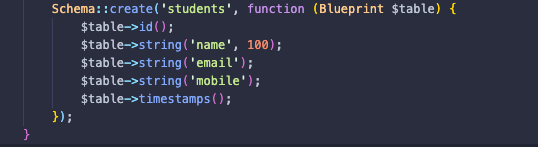
また、学生用のmigrationテーブルを設定する必要があります。
LivewireとJetstreamのパッケージのインストール
composer require laravel/jetstreamphp artisan jetstream:install livewireさらに、アセットをコンパイルする必要があるので、両方のnpmコマンドを同時に使用して、ビルドコンパイルタスクを完了させます。
npm install && npm run dev最後に、php artisanコマンドを使用して移行を実行します。
php artisan migrateLivewireのcrudコンポーネントを生成するため
php artisan make:livewire crud
上記のコマンドを実行すると、2つのファイルが生成されました。
ルートの作成
Route::get('students', Crud::class);最初のページに生徒のリストを表示したいので、render関数で全生徒のデータを取得します。
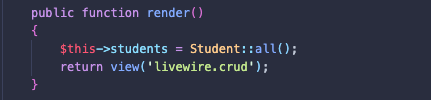
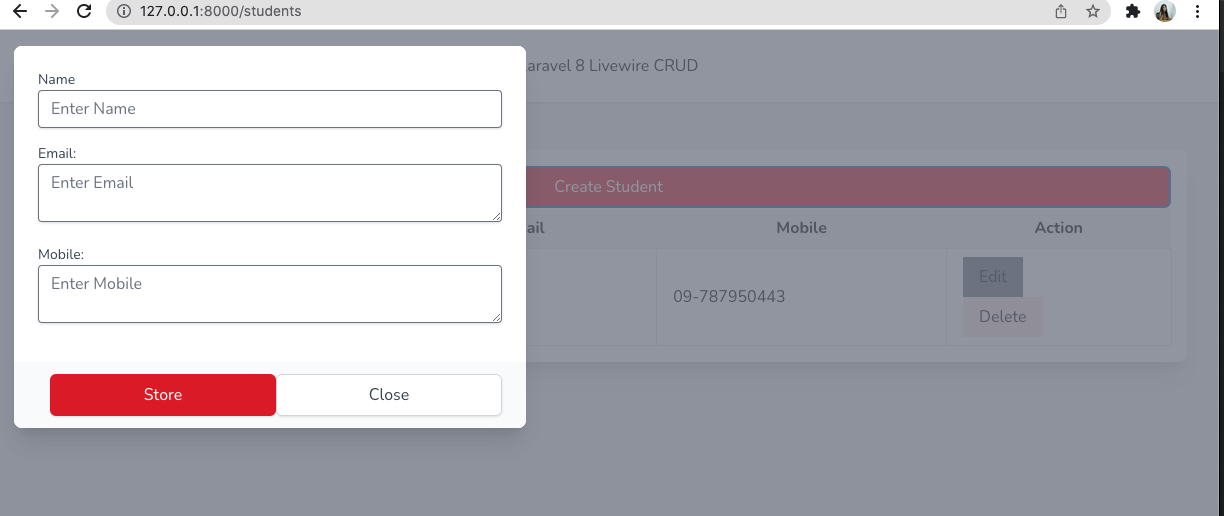
生徒を作成するため、
ボタンに wire:click=”create()” というアクションを追加します。
<button wire:click="create()"
class="my-4 inline-flex justify-center w-full rounded-md border border-transparent px-4 py-2 bg-red-600 text-base font-bold text-white shadow-sm hover:bg-red-700">
Create Student
</button>学生の作成をモデルフォームとしてデザインしたいので、いくつか条件を追加します。True を指定するとモデルボックスが開き、False を指定するとモデルボックスが閉じます。
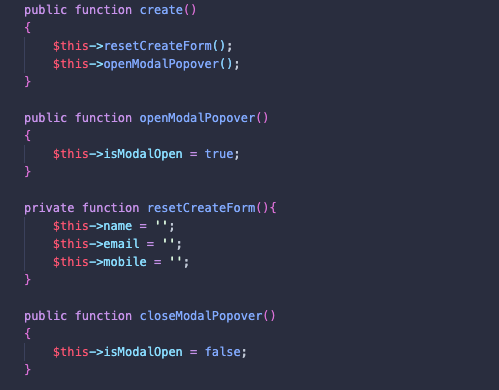
生徒を保存するため、
ボタンに wire:click.prevent=”store()” というアクションを追加します。
<button wire:click.prevent="store()" type="button"
class="inline-flex justify-center w-full rounded-md border border-transparent px-4 py-2 bg-red-600 text-base
leading-6 font-bold text-white shadow-sm hover:bg-red-700 focus:outline-none
focus:border-green-700 focus:shadow-outline-green transition ease-in-out duration-150 sm:text-sm sm:leading-5">
Store
</button>updateOrCreateを使用して、保存と更新の両方の関数を作成することにします。
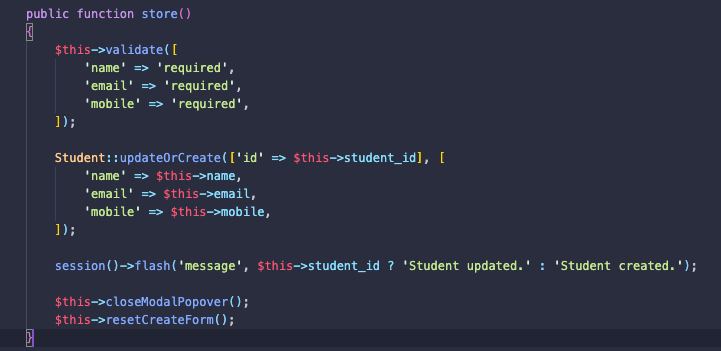
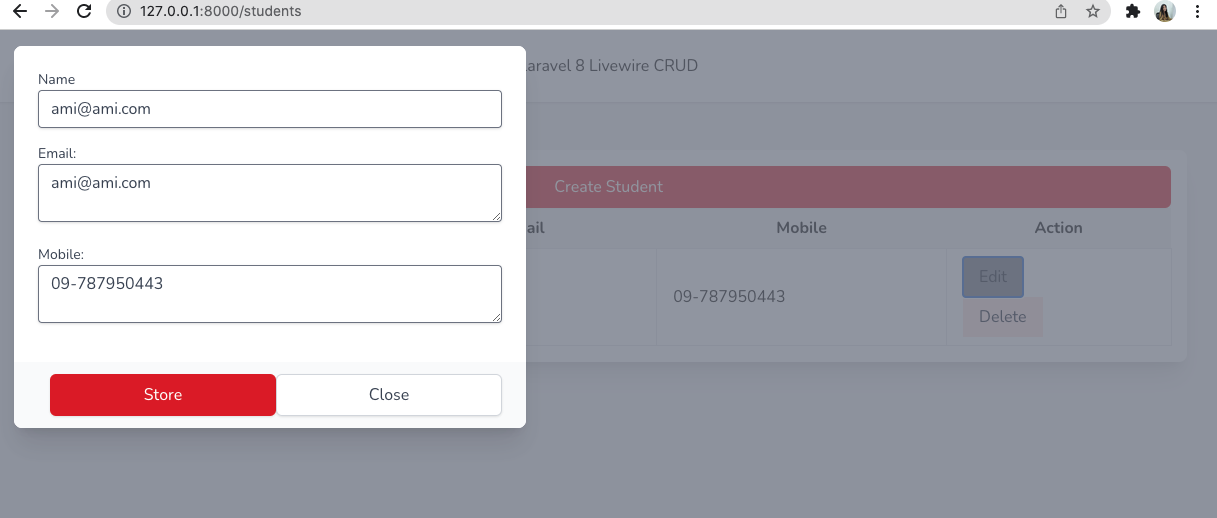
学生の編集を行うには
ボタンに wire:click=”edit({{ $student->id }})” というアクションを追加します。
後学生の削除を行うには
ボタンに wire:click=”delete({{ $student->id }})” というアクションを追加します。
<button wire:click="edit({{ $student->id }})"
class="flex px-4 py-2 bg-gray-500 text-gray-900 cursor-pointer">Edit</button>
<button wire:click="delete({{ $student->id }})"
class="flex px-4 py-2 bg-red-100 text-gray-900 cursor-pointer">Delete</button>編集と削除を行うために、生徒のデータを取得して、削除機能は生徒のデータを削除します。
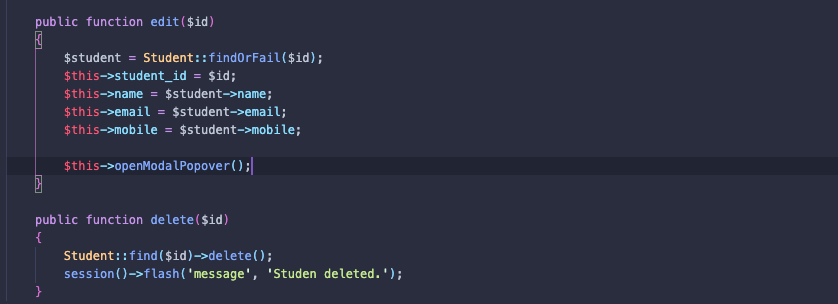
その結果は
学生一覧
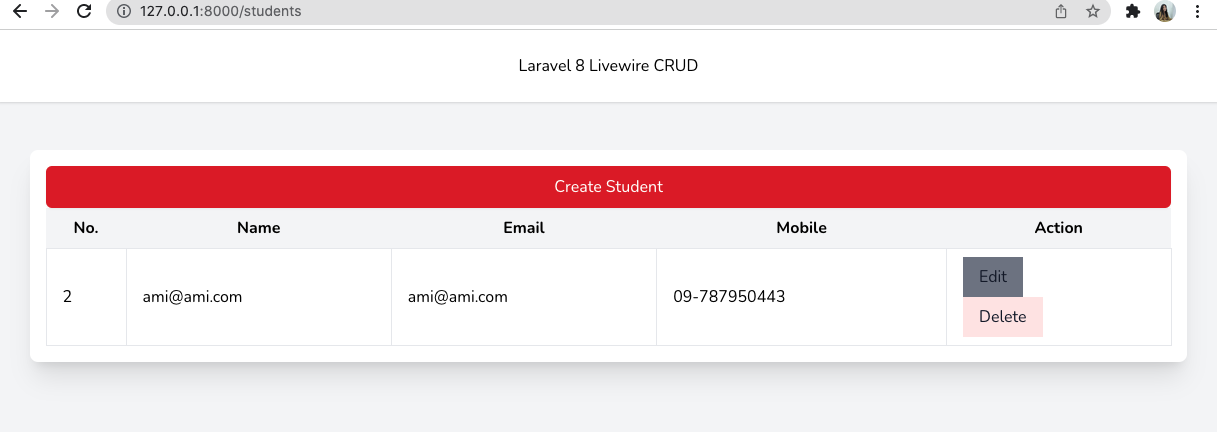
学生を作るために
学生を編集するには
最後までお読みいただき、ありがとうございました。
By Ami
asahi at 2022年01月07日 10:00:00