技術情報
- 2021年10月08日
- 技術情報
Flutter – Navigation drawer
Output:
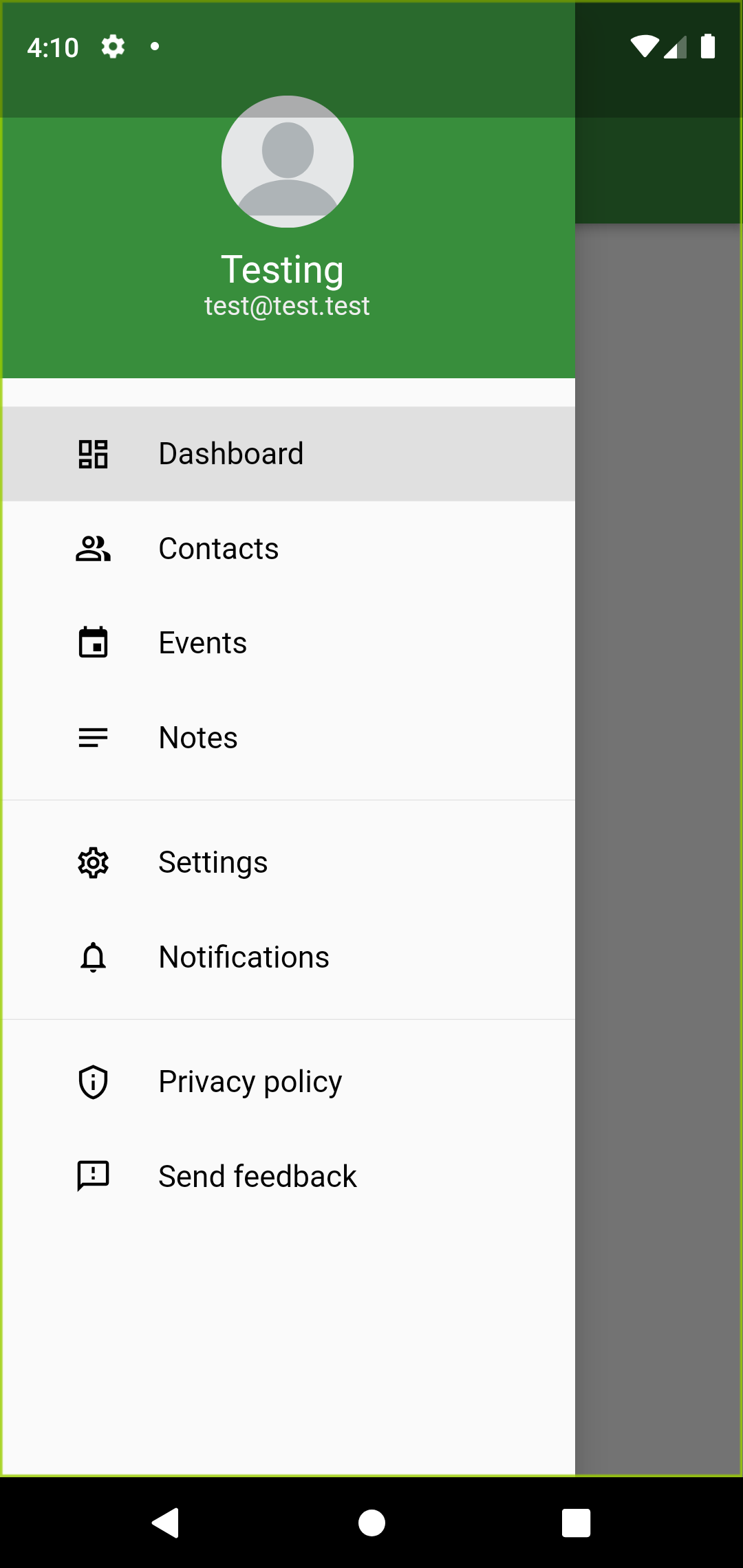
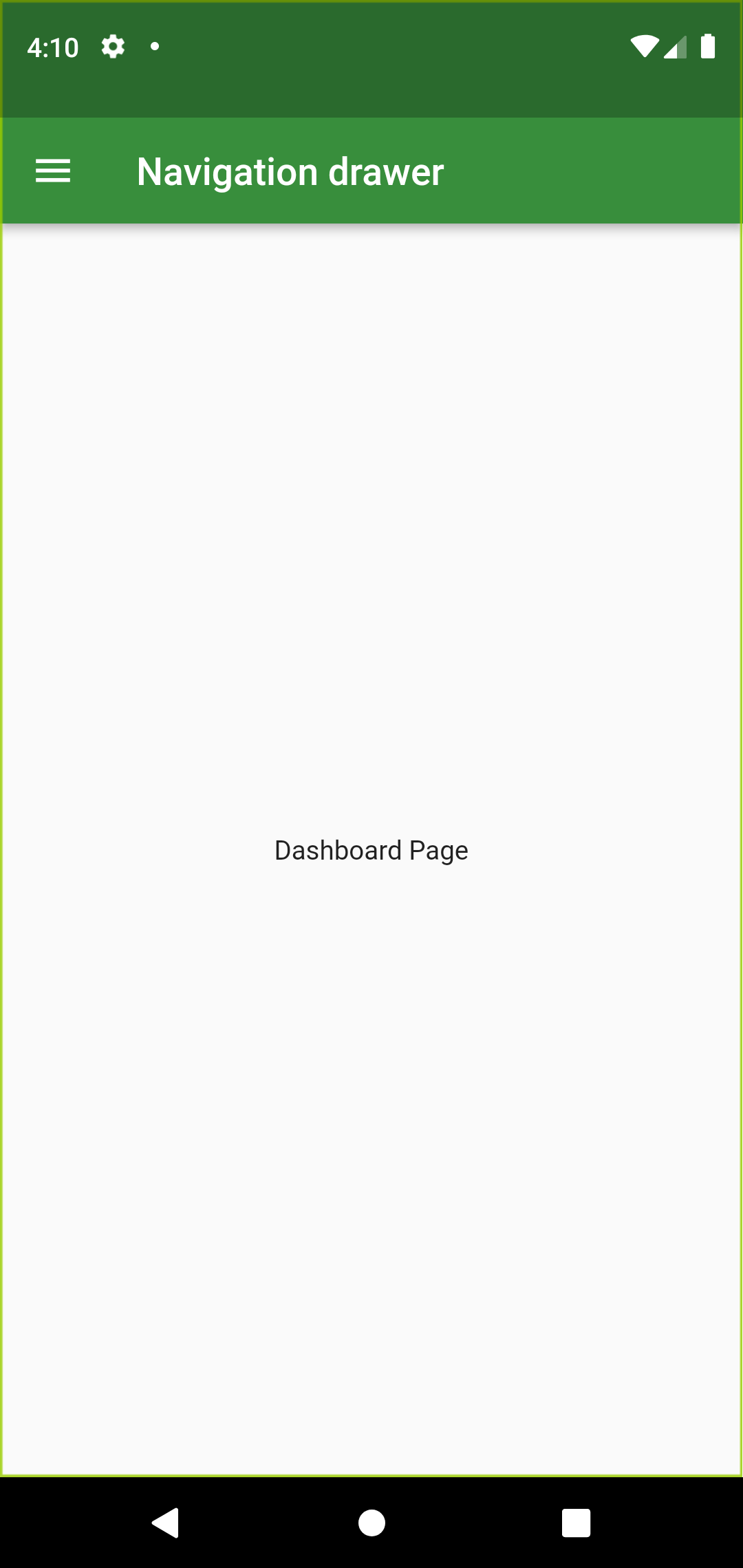
This week I would like to share about navigation drawer from Drawer widget. We can create navigation drawer by calling the constructor of the drawer class. Drawer widgets show us navigation drawer that slides to horizontally from edge fo the screen.
When we tap app bar, it will display the drawer. In this article we will create DrawerSection and eight navigation links. The links Dashboard, Contacts, Events, Notes, Settings, Notifications, Privacy policy and Send feedback are created using Column widget. Let’s design the drawer part first. I am creating drawer widget named MyDrawerList. And I am creating other drawer in a separate file so that we can reuse it in other pages.
Basic implementation of navigation drawer:
MyDrawerList(
child:Column(
children: [
menuItem(1, "Dashboard", Icons.dashboard_outlined,
currentPage == DrawerSections.dashboard ? true : false),
menuItem(2, "Contacts", Icons.people_alt_outlined,
currentPage == DrawerSections.contacts ? true : false),
etc..
],
) ,
),At first dashboard page is wanted to see, we can assign currentPage to DrawerSection.dashboard.
var currentPage = DrawerSections.dashboard;To display a navigation drawer we have to provide Drawer widget to scaffold’s drawer property.
Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.green[700],
title: const Text("Navigation drawer"),
),
body: container,
drawer: Drawer(
child: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
children: [
const MyHeaderDrawer(),
MyDrawerList(),
],
),
),
),
);If you want to navigate to another route first we have to dismiss the drawer by using below line of code
Navigator.pop(context);Now we have to navigate to another route using menuItem like below, in above we assign current page to dashboard page and menuItem widget is called in MyDrawerList widget.
Widget menuItem(int id, String title, IconData icon, bool selected) {
return Material(
color: selected ? Colors.grey[300] : Colors.transparent,
child: InkWell(
onTap: () {
Navigator.pop(context);
setState(() {
if (id == 1) {
currentPage = DrawerSections.dashboard;
}
}
etc..
}
Hope you enjoyed this post.
By Ami
asahi at 2021年10月08日 10:00:00
- 2021年10月01日
- 技術情報
Laravel – Jetstream
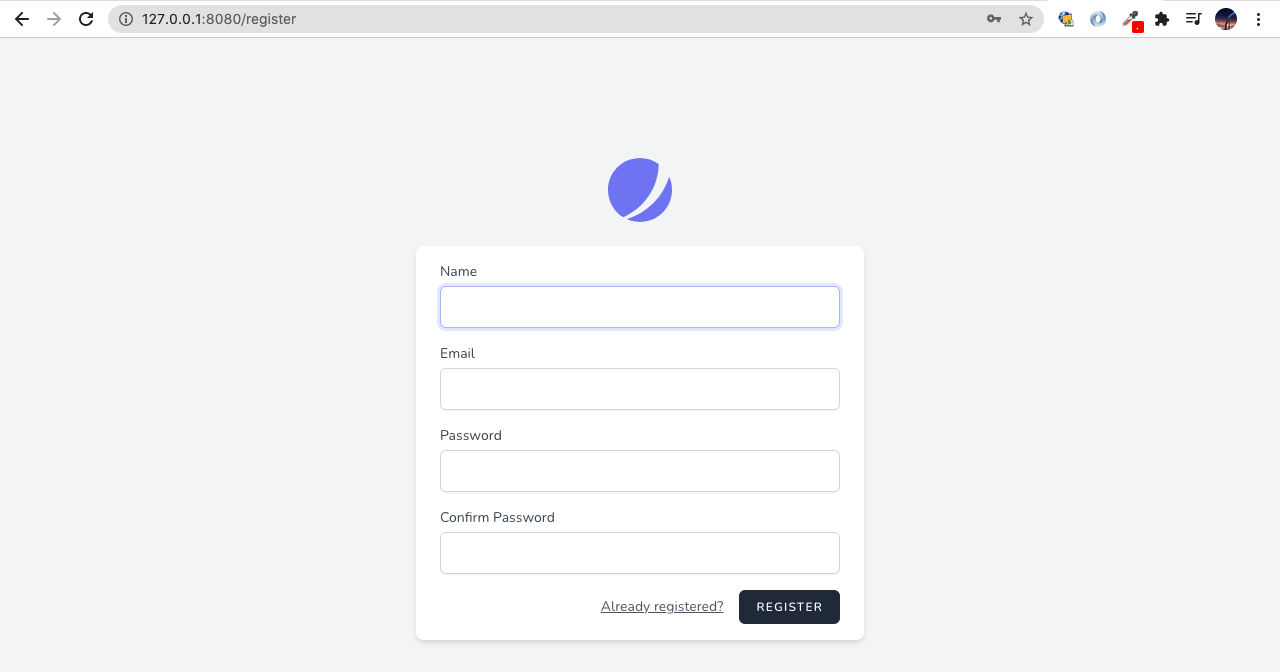
After Laravel version 7, Laravel version 8 introduced new features, this is the implementation of application’s login, registration, email verification, two-factor authentication, session management, and optional team management features.
This week I would like to share about using Jetstream how to set up in your project.
Firstly, it is better to install Jetstream into new Laravel project. Attempting to install Jetstream into an existing Laravel applicaiton will result in unexpected behavior and issues.
Installing Jetstream
You can install Jetstream via composer.
composer require laravel/jetstreamAfter installation is successful, you can choose one frontend stack from two of these Liveware and Intertia.js. This time I will set up using Liveware.
php artisan jetstream:install livewireAfter the installation is finished, you may install NPM dependencies and migrate the database. So, you may create new database, this name will be same from your .env file DB_DATABASE name.
npm install
npm run dev
php artisan migrateAfter running all of the commands, there will be finished the installation using Jetstream. The last thing is need to start the development server to see the result.
php artisan serve --port=8080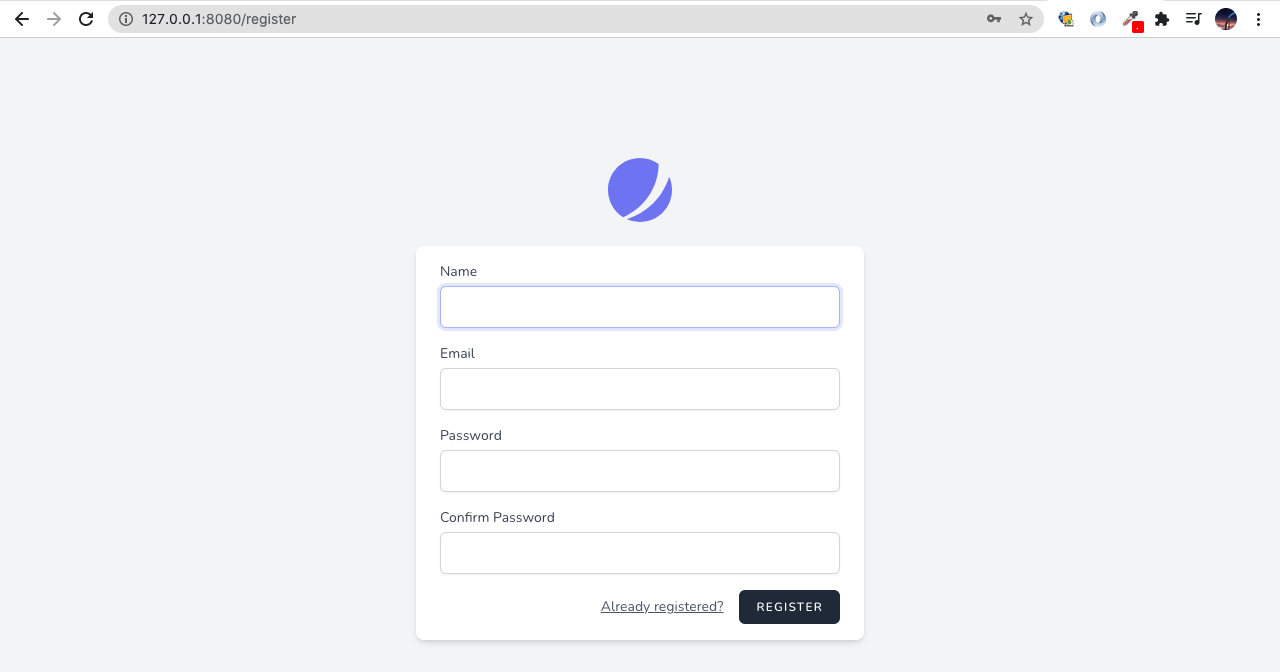
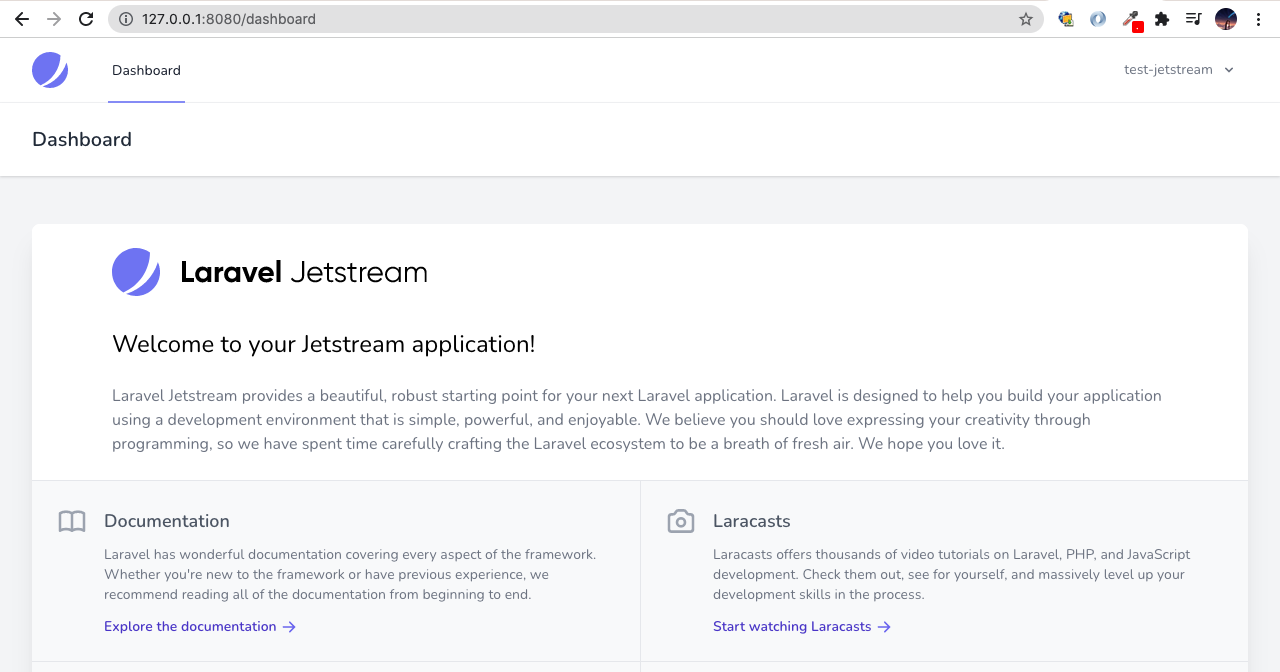
I hope you’ll enjoy reading it.
By Ami
asahi at 2021年10月01日 10:45:00
- 2021年09月27日
- 技術情報
Zero day attack
This is a common term for security vulnerabilities , discovered recently that attackers can use to attack systems. The term “zero-day” refers to the fact that the owner/developer has just become aware of the flaw which means there is zero day to fix the flaw.
If an attacker exploits a flaw before the developer addresses the issue, a zero-day attack will occur.
Zero-day is sometimes referred to as 0-day. The terms vulnerability, exploit, and attack are commonly used in conjunction with zero-days to help you understand the difference.
Zero day vulnerability
This is a software vulnerability discovered by an attacker before the vendor is aware of it. Since the vendor does not know, there is no patch for the zero-day vulnerability and the attack is more likely to be successful.
Zero day exploit
This becomes a method used by hackers to attack systems with previously unidentified vulnerabilities.
Zero day attack
A zero-day attack is the use of a zero-day exploit to damage or steal data from a vulnerable system.
How this happened
Attackers might be able to detect vulnerabilities before software developers. While the vulnerability is still open, they can write and implement code that exploits it. This is known as exploit code.
Exploit code can target software users, for example through the theft of personal information or other forms of cybercrime. Once an attacker has identified a zero-day vulnerability, they need a way to reach the vulnerable system. They often send this through socially designed emails, other messages that appear to be from known or legitimate correspondents, but are actually from attackers. This message attempts to convince the user to take actions such as opening a file or visiting a malicious website. By doing so, it downloads the attacker’s malware, breaks into user files and steals sensitive data.
If the vulnerability is known, the developer will try to patch it for the flaw. However, security vulnerabilities are often not immediately discovered. It can take days, weeks, or even months for developers to identify the vulnerability that caused the attack. Also, even after a zero-day patch is released, not all users are in a hurry to update the patch.
Exploits can be sold on the dark web for large sums of money. Once the exploit is discovered and repaired, it is no longer called a zero-day threat.
Zero-day attacks are especially dangerous because only the attacker knows the that flaw. Once they gain access, criminals can attack immediately or sit down and wait for the best time to get most advantages.
Identifying the zero day vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities can take many forms, including missing data encryption, missing authorization, broken algorithms, bugs, and password security issues, and can be difficult to detect. Due to the nature of these types of vulnerabilities, detailed information about zero-day exploits will only be available after the exploit has been identified.
Organizations which had been attacked by zero-day exploits can experience unexpected traffic or suspicious scanning activity originating from customers or services. Machine learning is increasingly used to detect data from previously recorded exploits and to establish a safe system behavior baseline based on data from past and present interactions with the system.
Examples of zero day vulnerability
2021: Chrome zero-day vulnerability
In 2021, Google’s Chrome was hit by a series of zero-day threats, urging Chrome to publish updates. This vulnerability was caused by a bug in the JavaScript V8 engine which is used in web browsers.
2020: Zoom
A vulnerability has been found in a popular video conferencing platform. In this zero-day attack example, attacker was remotely accessing a user’s PC while running an older version of Windows. If the target is an administrator, attacker could completely hijack your machine and access all files.
2020: Apple iOS
Apple’s iOS is often said to be the most secure of the major smartphone platforms. However, in 2020, it was the victim of at least two sets of iOS zero-day vulnerabilities, including a zero-day bug that allowed an attacker to compromise the iPhone remotely.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2021年09月27日 10:38:00
- 2021年09月20日
- 技術情報
Handling Japanese characters in PHP
We know we have manipulate strings, characters in PHP using various function depending on what we need. For example – cutting strings, counting strings length, replacing strings etc. We can directly use built-in PHP function like substr, str_replace, str_length etc. But we can’t directly use these functions for Japanese characters, Why ?
Everyone knows that a “bit” is 0 or 1, nothing else, and a “byte” is a group of eight consecutive bits. Since one byte has eight of these dual value points, the byte can consist of a total of 256 different patterns (2 power 8). Different characters can be associated with each possible 8-bit pattern.
It is working fine as long as the language characters can be represented by 256 or less.
But what if you can’t represent a language with just 256 characters? Obviously Japanese characters need more than that. Nowadays , 256 characters isn’t enough anywhere. Fortunately, the new super character sets use anywhere from 1 to 4 bytes to define characters. Unicode, a scheme that uses multiple bytes to represent characters. There are several version of it like UTF-32, 26 8.
Unicode (including UTF-8) uses multiple byte configurations to represent characters. UTF-8 uses 1 to 4 bytes to generate 1,112,064 patterns that represent different characters.
We can’t still directly use string related functions by declaring UTF-8. PHP isn’t really designed to handle multibyte characters, so using standard string functions to handle these characters can have uncertain results. If you need to handle these multibyte characters, you need to use a special set of functions, the mbstring function. Use the --enable-mbstring compile-time option to enable the mb function and set the run-time configuration option mbstring-encoding_translation.
The next thing is HTTP header might covers the communication also contains the character set ID, so we need to declare the header also like this.
mb_internal_encoding("UTF-8");
Finally we can use mb string related function instead of directly using string function.
For example we can use mb_strlen instead of strlen .
You can see various mb functions here.
That’s all for today.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2021年09月20日 10:00:00
- 2021年09月17日
- 技術情報
Flutter – share option button
This week I would like to share you about how to add share option button in flutter. Let’s get started!

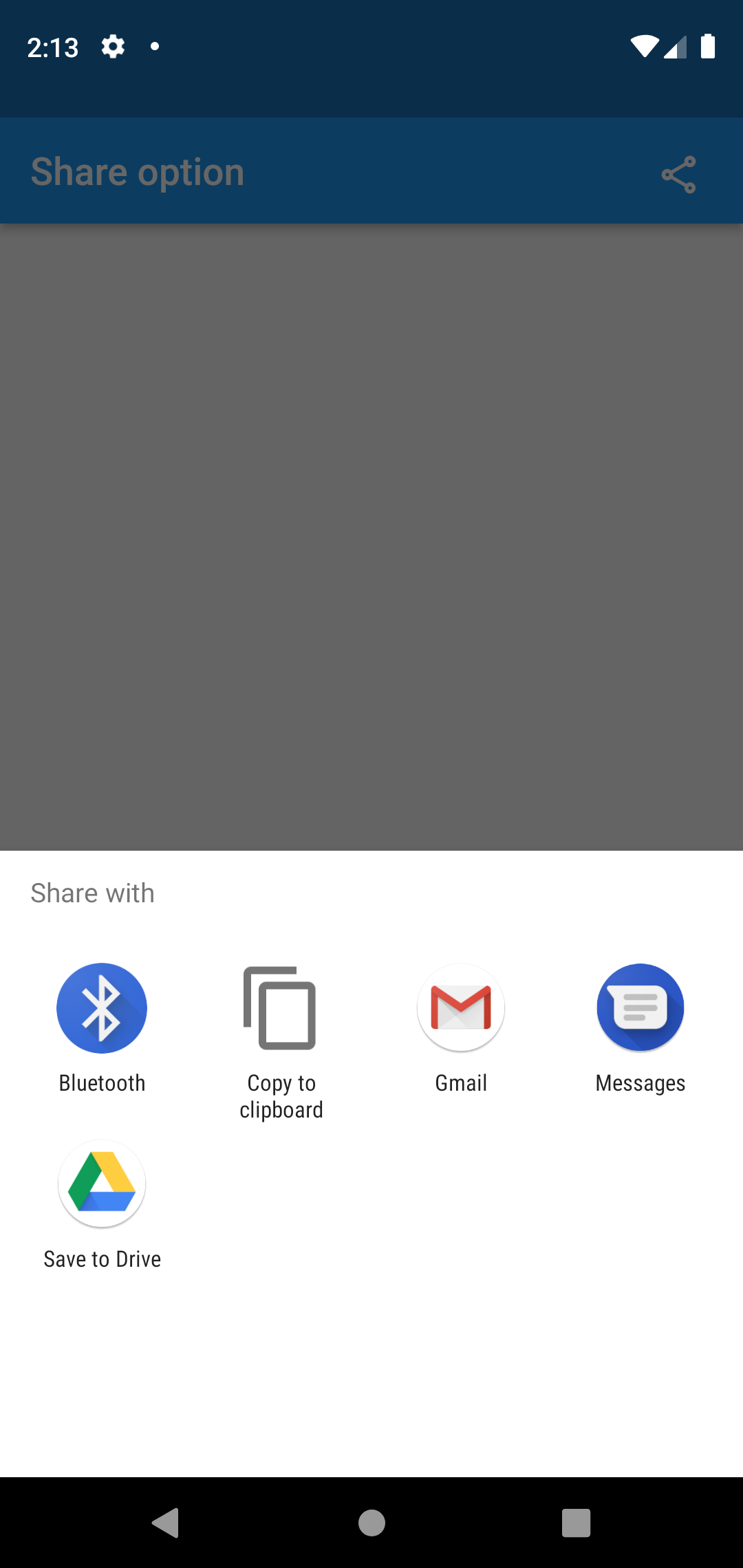
First thing we need to do is to add this share pub in your pubspec.yaml file.
dependencies:
share: ^2.0.4We can simply apply the share pub in the code.return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title : const Text('Share option '),
actions: [
Padding(padding: const EdgeInsets.all(10),
child: IconButton(
icon : const Icon(Icons.share_outlined),
onPressed: () {
Share.share("https://dummy~~~~~~~.com");
},
)
)
],
),
);Hope you enjoyed this article!
By Ami
asahi at 2021年09月17日 10:00:00