アプリ関連ニュース
- 2022年3月07日
- Apple
Apple’s March 8 event
The next Apple event is Tuesday, March 8th. This will be a virtual event that can also be viewed from Apple’s website or Apple TV and YouTube. Today I gonna share with you some rumors expectations for this coming event.
New iPhone SE
Every few years, Apple releases a low-priced iPhone with the latest components in its old body, and this year is no exception. Apple plans to launch a third iPhone SE for $ 399, with the same iPhone 6-like design as before, but with 5G support, an improved camera, and an A15 Bionic processor.

iPad air 5
New year, new iPad. The iPad will be equipped with an A15 chip, two additional speakers (four in total), and a 5G connection. The camera may also be improved.
Mac mini
Apple plans to announce a number of Macs this year, with at least one likely to be seen at the March 8 event. The catchphrase “Peak Performance”; and the direction is that Apple usually won’t launch high-performance mobile products until the fall.
Rumor has it that the “Mac Mini Pro” with M1 Max and M1 Pro chips is now being pointed out. After all, it doesn’t make sense for Apple laptops to be stronger than desktop products for a long time. This Mac Mini is expected to offer a slimmer and more sophisticated design.
New MacBook with M2
Apple’s M1 chip was announced in 2020. That is, you are trying to get an update. Rumor has it that the new MacBook Pro with an entry-level M2 chip should be better than the previous M1 MacBook Pro, but it doesn’t quite match the M1 Pro or Max.
To keep costs relatively low, the new MacBook Pro doesn’t have a flashy 120Hz display or Mini LED panel. The benefit of inferior screen technology is that it can avoid the dreaded notch, perhaps.
It’s also very likely that Apple will announce a redesigned MacBook Air with an M2 chip later this year, but it’s not sure.
iOS 15.4
On the software side, we are planning a release date for iOS 15.4. This is primarily a mid-cycle update and primarily includes Face ID support while wearing a mask. It also includes over 30 new emojis, non-binary Siri voice, and support for multi-device interaction with Universal Control. But most of the software might come at WWDC later this year.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2022年03月07日 10:30:00
- 2022年3月04日
- 技術情報
Laravelのファイルアップロード: 重複するファイル名 – 解決するための2つの方法
今日は、ファイルのアップロードについて、特に、同じファイル名でファイルをアップロードできるようにするとどうなるか、古いファイル名を上書きしてしまうか、それをいろいろとお話したいと思います。
例えば、デフォルトで登録フォームがあり、アバターがあり、誰かがavator.jpgというファイル名でファイルをアップロードしたとします。これは正常にアップロードされているのですが、開発者がよくやるのは、ClientOriginalNameが悪意のないものであることを信じてファイル名をアップロードすることです。
しかし、元のファイル名を保持したい場合は、それは大丈夫かもしれません。しかし、同じファイル名で登録した人がいて、そのファイルがstorage/app/public/avatorsにavator.jpgとしてアップロードされた場合、問題が発生することがあります。
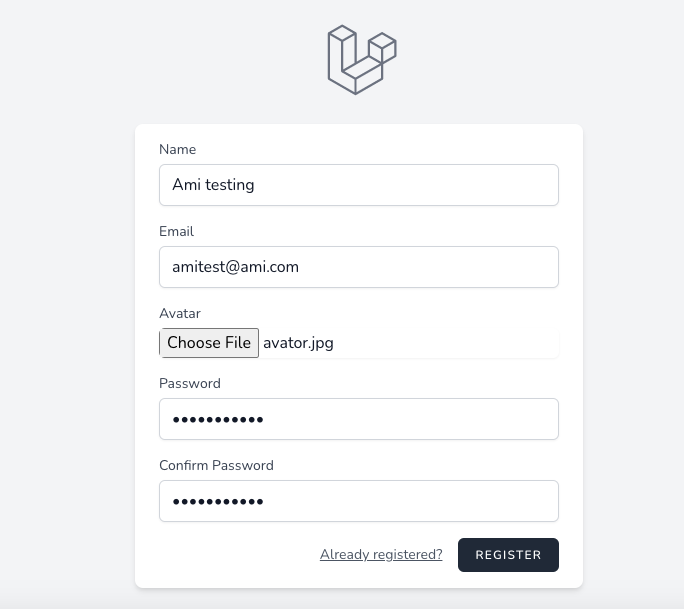
そして、別のユーザーで登録しようとし、ユーザー情報を入力し、異なるパスからアバターをアップロードしますが、ファイル名は同じです。登録後、古いアバターはやみくもに上書きされ、サーバーから削除されることさえあります。というわけで、これは今問題になっています。どのようにコードでそれを解決するかは、いくつかの異なる方法があります。
ということで、今からこの方法をお話ししたいと思います。
1つ目はファイル名を変更する方法です。
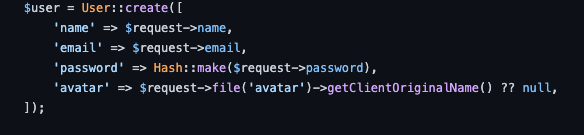
if ($request->file('avatar')) {
$fileName = pathinfo($request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalName(), PATHINFO_FILENAME) . '-' . $user->id . '.' . $request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalExtension();
$request->file('avatar')->storePubliclyAs('avatars', $fileName, 'public');
$user->update([
'avatar' => $fileName ?? null,
]);
}アベータがある場合、拡張子なしのファイル名からファイルを作成し、ユーザ登録からuser_id、そしてオリジナルの拡張子からファイルを構築することになります。そして、そのファイルをファイル名と一緒にパブリックドライバに保存し、ユーザを更新します。
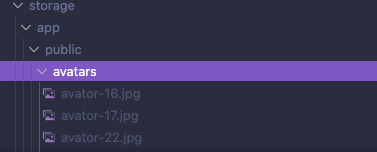
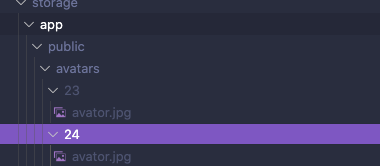
2つ目はサブフォルダを作成する方法です。
$request->file('avatar')->storePubliclyAs("avatars/{$user->id}", $request->file('avatar')->getClientOriginalName(), 'public');publicのuser_idサブフォルダに元のファイル名で保存します。
結果一覧
はい。ということで今回は以上になります。
By Ami
asahi at 2022年03月04日 10:00:00
- 2022年3月03日
- 技術情報
DataTablesを使用したテーブル生成とサーバーサイド連携(4)
今回はDataTablesを使用したテーブル生成方法とサーバーサイド連携方法の連載Part4です。
前回の記事「DataTablesを使用したテーブル生成とサーバーサイド連携(3)」で発生した問題の原因と解決の方法について紹介いたします。
nishida at 2022年03月03日 10:00:00
- 2022年3月03日
- Web Service
Awesome features of PHP 8
PHP 8 has been officially released for general users. PHP 8 brings a host of new features improvements, functions, and deprecations to the language compared to PHP 7. Among all of these new features, the JIT compiler is the one sharing the limelight. However, other features like syntax changes are also to be taken into account as it is these features that will have a greater impact on the practitioners.
New features include:
- Named arguments
- Union types
- Constructor property promotion
- Custom object serialization
- Match expression
- Nullsafe operator
- Improvements in the type system and error handling
New PHP Functions
- New str_contains() function
- New str_starts_with() and str_ends_with() functions
- New fdiv() function
- get_debug_type() function
— str_contains()
Helps us in determining whether the given sub-string is present inside the string.
Example :
str_contains ( string $austin , string $tin ) : boolExecutes a case-sensitive operations and checks whether the string austin contains the substring tin.
— string_starts_with and str_ends_with()
Using this function we can easily find whether the given sub-string is at the beginning or ending of the string.
Example:
str_starts_with(string $austin, string $au): bool;
str_ends_with(string $austin, string $tin): bool;These new functions can be impersonated with strpos, substr, strncmp, and substr_compare. However, the new functions were favourably received due to its engine-level optimizations and their regular use cases.
— fdiv()
The new fdiv() function has similar ability as the fmod() and intdiv() functions, that allows for division by 0. Instead of getting errors, you’ll get INF, -INF, or NAN, depending on the scenario.
— get_debug_type()
The new get_debug_type function always returns the true native type of variables. It returns a return native type names, e.g., int rather than integer, double instead of float.
get_debug_type() function helps in
By Tsuki
tsuki at 2022年03月03日 10:00:00
- 2022年3月01日
- 技術情報
Comparisons between Ubuntu and Linux Mint
Today, I would like to share about comparisons between Ubuntu and Linux Mint Operating systems. Let’s take a look.
Ubuntu is the most famous Linux distribution. Its development started back in 2004. It is based on Debian distribution, which is why Ubuntu also uses the dpkg packaging system (And .deb package format) along with the apt packager manager.
Linux Mint, on the other hand, is based on Ubuntu. Its development started in 2008. Hence, Mint by extension is also based on Debian, and uses the same package manager and packaging system.
1. Distribution Goals
Ubuntu does not aim to be a simple Linux desktop distribution. Instead, Ubuntu is a general-purpose Linux distribution that can be used on servers, cloud, IoT and embedded devices.
Linux Mint, on the other hand, is nothing more than a desktop Linux distribution. There are no Linux Mint versions for servers or cloud or IoT… etc.
2. Software Manager
Ubuntu Software Center is slow while interacting with it. Of course, things have improved over the years but even with Ubuntu 20.04, on board, you will often notice it loading up slow or freezing when updating/installing an app. On the other hand, Linux Mint’s Software Manager is lighter and quicker.
3. User Interfaces
Ubuntu comes with the GNOME desktop environment. GNOME is an open-source desktop environment, which means that it’s a collection of programs associated with a GUI. The GNOME GUI has a dock on the left side where you can see all opened applications.
Mint comes with Cinnamon as a default desktop environment. Cinnamon is a Windows-like interface with a launcher, panel, and a system notification area on the bottom.
Ubuntu does support other desktop environments like Budgie, KDE, and Xfce. Mint only supports KDE and Xfce in addition to its default, Cinnamon.
4. Memory Usage
Desktop environments usually consume a lot of memory in order to run, which reduces the performance of the OS. Both Cinnamon and GNOME have their own perks but Cinnamon consumes significantly lesser memory than Ubuntu Desktop, making Mint the best distro for old PCs. So, the advantage of Mint is Cinnamon’s lower memory consumption as compared to GNOME.
5. Preinstalled Applications
Every Linux distribution comes with preinstalled applications like internet browsers, video players, image editors, and text editors. While Ubuntu offers more applications, their applications are difficult to search for, as you have to remember the exact name of the application. You can’t just guess the name or depend on browsing to find it.
Mint, on the other hand, only offers basic applications, but those applications are easy to find on their Windows-like menu.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2022年03月01日 10:00:00