未分類
- 2022年04月07日
- 未分類
Laravelでよりクリーンなコードを書く
行を正しく分割する
行は適当に分けないが、長くしすぎないようにする。配列を[]で開き、値をインデントするとうまくいく傾向がある。長い関数のパラメータ値も同様です。他にも、連鎖した呼び出しやクロージャも行を分割するのに適しています。
Bad
// No line split
return $this->request->session()->get($this->config->get('analytics.campaign_session_key'));
// Meaningless line split
return $this->request
->session()->get($this->config->get('analytics.campaign_session_key'));// Good
return $this->request->session()->get(
$this->config->get('analytics.campaign_session_key')
);
// Closure
new EventCollection($this->events->map(function (Event $event) {
return new Entries\Event($event->code, $event->pivot->data);
}));
// Array
$this->validate($request, [
'code' => 'string|required',
'name' => 'string|required',
]);ルックアップテーブルを使用する
else if ]ステートメントを繰り返し書く代わりに、配列を使って、持っているキーに基づいて、欲しい値を探します。コードはよりすっきりして読みやすくなり、何か問題が発生したときには理解しやすい例外を見ることができます。中途半端なエッジケースはありません。
// Bad
if ($order->product->option->type === 'pdf') {
$type = 'book';
} else if ($order->product->option->type === 'epub') {
$type = 'book';
} else if ($order->product->option->type === 'license') {
$type = 'license';
} else if ($order->product->option->type === 'artwork') {
$type = 'creative';
} else if $order->product->option->type === 'song') {
$type = 'creative';
} else if ($order->product->option->type === 'physical') {
$type = 'physical';
}
if ($type === 'book') {
$downloadable = true;
} else if ($type === 'license') {
$downloadable = true;
} else if $type === 'creative') {
$downloadable = true;
} else if ($type === 'physical') {
$downloadable = false;
}// Good
$type = [
'pdf' => 'book',
'epub' => 'book',
'license' => 'license',
'artwork' => 'creative',
'song' => 'creative',
'physical' => 'physical',
][$order->product->option->type];
$downloadable = [
'book' => true,
'license' => true,
'creative' => true,
'physical' => false,
][$type];可読性を向上させる場合は変数を作成する
複雑な呼び出しから値が得られることもあり、そのような場合は変数を作成すると可読性が向上し、コメントの必要性がなくなります。文脈が重要であり、最終的な目標は読みやすさであることを忘れないでください。
// Bad
Visit::create([
'url' => $visit->url,
'referer' => $visit->referer,
'user_id' => $visit->userId,
'ip' => $visit->ip,
'timestamp' => $visit->timestamp,
])->conversion_goals()->attach($conversionData);// Good
$visit = Visit::create([
'url' => $visit->url,
'referer' => $visit->referer,
'user_id' => $visit->userId,
'ip' => $visit->ip,
'timestamp' => $visit->timestamp,
]);
$visit->conversion_goals()->attach($conversionData);アクションクラスの作成
一つのアクションのためにクラスを作ることで、物事がきれいになることもあります。モデルは、それに関連するビジネスロジックをカプセル化する必要がありますが、あまり大きくなりすぎるのもよくありません。
// Bad
public function createInvoice(): Invoice
{
if ($this->invoice()->exists()) {
throw new OrderAlreadyHasAnInvoice('Order already has an invoice.');
}
return DB::transaction(function () use ($order) {
$invoice = $order->invoice()->create();
$order->pushStatus(new AwaitingShipping);
return $invoice;
});
}// Good
// Order model
public function createInvoice(): Invoice {
if ($this->invoice()->exists()) {
throw new OrderAlreadyHasAnInvoice('Order already has an invoice.');
}
return app(CreateInvoiceForOrder::class)($this);
}
// Action class
class CreatelnvoiceForOrder
{
public function _invoke(Order $order): Invoice
{
return DB::transaction(function () use ($order) {
$invoice = $order->invoice()->create();
$order->pushStatus(new AwaitingShipping);
return $invoice;
});
}
}イベント利用
コントローラからイベントへのロジックのオフロードを検討します。例えば、モデルを作成するときです。この利点は、モデルの作成がどこでも(コントローラ、ジョブ、…)同じように動作し、コントローラはDBスキーマの詳細について心配する必要がなくなるということです。
// Bad
// Only works in this place & concerns it with
// details that the model should care about.
if (! isset($data['name'])) {
$data['name'] = $data['code'];
}
$conversion = Conversion::create($data);
// Good
$conversion = Conversion::create($data);
// Model
class ConversionGoal extends Model
{
public static function booted()
{
static::creating(function (self $model) {
$model->name ??= $model->code;
});
}
}来週は、クリーンコードに関するより多くのヒントを紹介する予定です。
By Tsuki
tsuki at 2022年04月07日 10:51:15
- 2022年01月06日
- 未分類
5 Website To Help You Create Beautiful JavaScript Code Snippets For Your Medium Articles
While writing technical development articles you will often show some code blocks. You can either take a screenshot of your favorite IDE while it shows the code or you can use the simple Medium code formatting by pressing ```. But instead of using any of those two approaches, I would suggest using any or all of the websites presented within this article.
1. GitHub Gists
The main website to create code blocks is GitHub Gists. You can simply go to https://gist.github.com and add your code into the Gist. Also, you can add multiple files to one single Gist and use them independently in your article.
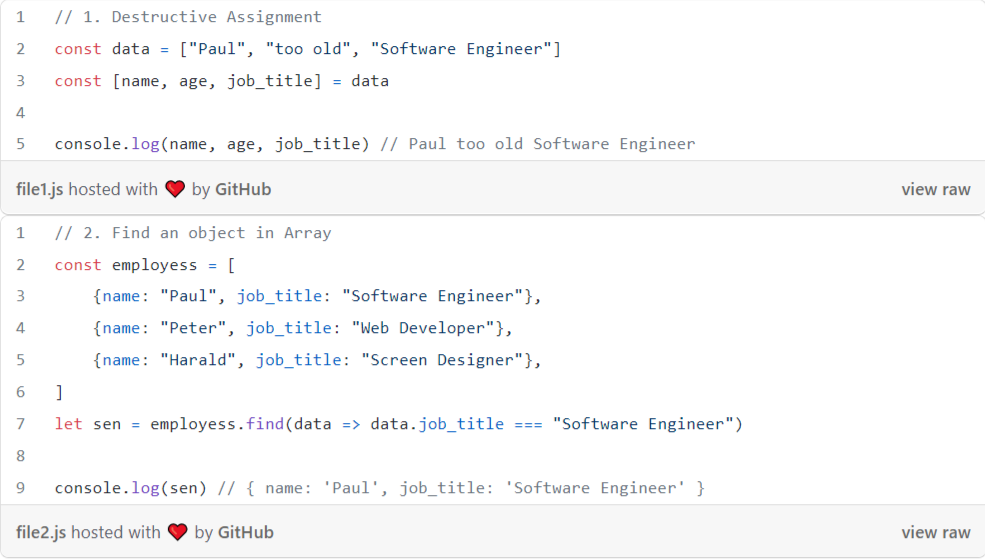
2. carbon.now.sh
This website is really simple. You can log in with your GitHub profile and start creating snippets. Go to and insert your code. It will be automatically saved into your profile and can be accessed by the URL.
As an example, https://carbon.now.sh/XHGvwhmthQjAZLJAWNoA
The content will look like this in Medium:
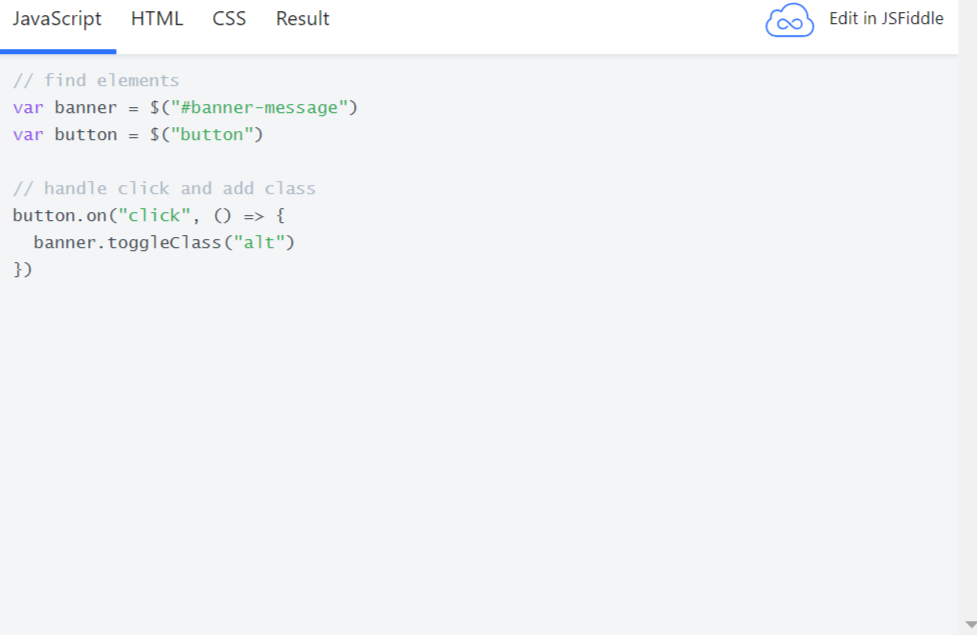
3. JSFiddle
JSFiddle is a famous javascript code playground where you can test your HTML, CSS, and JS in the browser.
Additionally, these code blocks can be imported into Medium as an embed. Within Medium you will have one block with a tab menu that can be switched.
I use this fiddle as an example: https://jsfiddle.net/paulknulst/odLg3qu1/
As you can see you can switch between JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and Result. Within Result, you can see the outcome after the three “files” are combined and run by jsfiddle.net.
4. Codepen.io
Codepen is comparable to JSFiddle. You can also add HTML, CSS, and JS and import them into Medium.
I use this as an example: https://codepen.io/paulknulst/pen/NWaXwdW
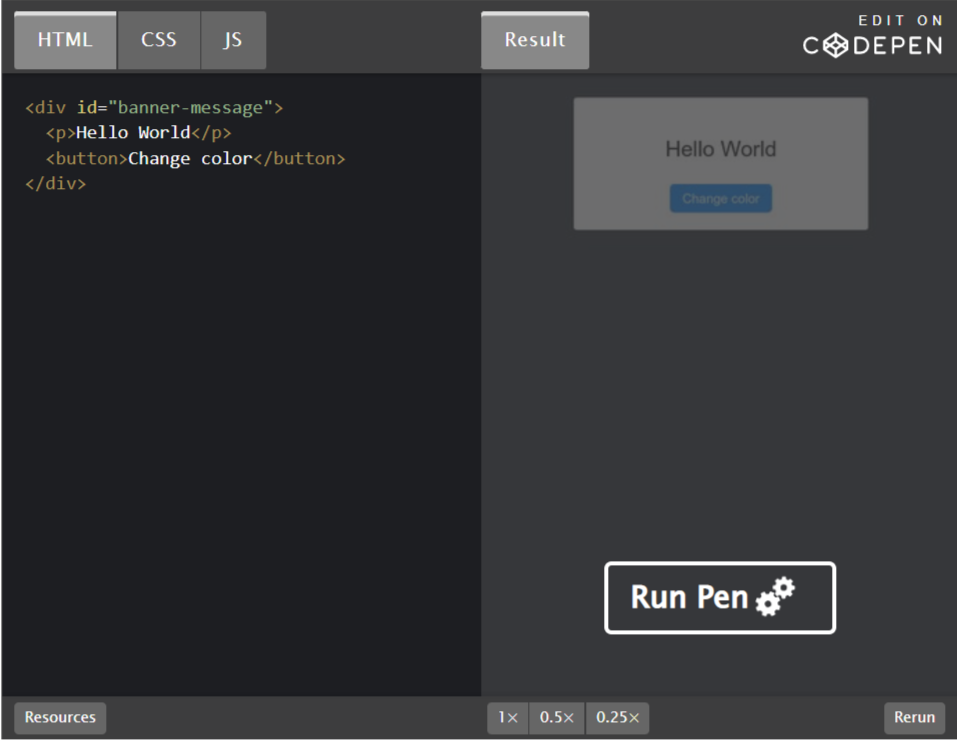
As you can see you can switch between JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and Result. It looks different from JSFiddle but contains the same information.
5. Codesandbox.io
With Codesandbox.io you are able to create complete sandboxes for your project that will run within the browser.
If you start with this website you can choose a sample sandbox from a list of predefined sandboxes
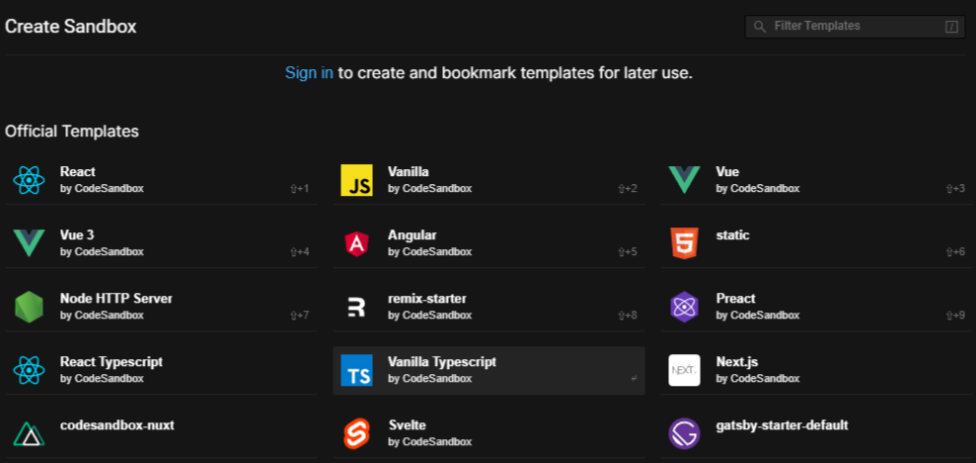
After you choose your template all needed files will be created and you can change them in the integrated IDE and see the result in an embedded browser window.
I really hope you find this article helpful and can use any of the websites in your development articles.
Tsuki
tsuki at 2022年01月06日 10:00:00
- 2021年12月23日
- 未分類
4 Reasons Why We Need Code Reviews
Code reviews are necessary as they offer multiple benefits that help improve your code and your team. These benefits include:
- Helping reduce bugs and logic errors
- Providing an opportunity for training
- Spreading knowledge across areas and teams
- Revealing new ideas and techniques
Code reviews help reduce bugs and logic errors
One of the main things a reviewer should be looking for when reviewing code is that the code does the right thing without any errors.
It may seem like it would be hard to find bugs while reading code, but as developers become more experienced reviewing code, issues will start to stand out.
Even with QA and automated testing, finding bugs during a code review is helpful. Reviews help verify the code and tests are both correct. A code review can direct the developer to the exact area of the problem, making it easier to debug and fix. Reviews are just one more step we can use to help avoid stressful after hour bugs.
Reviews offer opportunities for training
We all know how quickly the technology around us changes. there is a new language, tool, or framework every day. We also learn new best practices, standards, and ways to do things as we gain more experience.
How do we keep all the developers on the team up to date with these changes? Of course, there are courses, tutorials, blogs, the team wikis, and guides out there. But do we have time for every developer on our team to always go through a course? Developers should continue to use these resources and learn from them. However, none of these resources have come close to what we learned by working with the team and having code reviewed. Good code has come from code reviews.
Code reviews spread knowledge across areas and teams
If we had two teams of developers who always worked together and reviewed each other’s code versus two groups of developers who never reviewed the other team’s code, who do you think will have better code in the long run?
It probably will be the teams that review each other’s code. Those two teams will be passing knowledge back and forth about their specific areas and the best way to do things. They will be learning from different experiences and projects.
Code reviews also reveal new ideas and techniques
Reviews will teach the same team new things the same way they will teach multiple teams. But new ideas and techniques often come up in code reviews even among the same team members.
Think about most of the code we write. How often do we research different design patterns, consider different architectures or attempt multiple solutions before deploying code? At most places, we don’t have the time to pair program on everything or always meet about how to code every feature. Once a team implements a review process, these suggestions happen without extra steps.
Tsuki
tsuki at 2021年12月23日 10:00:00
- 2021年11月30日
- 未分類
Code Obfuscation
Obfuscation is making something complex and difficult to understand. Programming codes are often obfuscated to decrease the security risks such as preventing an attacker from reverse engineering a software program and protect intellectual properties.
Code obfuscation is not about changing the program’s original code contents, but rather about making the presentation of that code more confusing. Obfuscation does not change how the program works or outputs.
The following are some techniques we should know about obfuscation.
Renaming
The obfuscator alters the methods and names of variables. The new names may include unprintable or invisible characters.
Packing
This compresses the entire program to make the code unreadable.
String encryption
This method uses encryption to hide the strings in the executable and only restores the values when they are needed to run the program. This makes it difficult to go through a program and search for particular strings.
Control flow
The decompiled code is made to look like spaghetti logic, which is unstructured and hard to maintain code where the line of thought is obscured. Results from this code are not clear, and it’s hard to tell what the point of the code is by looking at it.
Instruction pattern transformation
This approach takes common instructions created by the compiler and swaps them for more complex, less common instructions that effectively do the same thing.
Dummy code insertion
Dummy code can be added to a program to make it harder to read and reverse engineer, but it does not affect the program’s logic or outcome.
Metadata or unused code removal
Unused code and metadata give the reader extra information about the program, much like annotations on a Word document, that can help them read and debug it. Removing metadata and unused code leaves the reader with less information about the program and its code.
Summary
Obfuscation techniques are used in various cases. For example, these can be used to stop someone from copying your client-side code. And enterprises also need to make sure that websites are protected against malicious code injection and it difficult to discover useful information such as trade secrets (IP), credentials, or security vulnerabilities from an application.
Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2021年11月30日 10:00:00
Laravel Package to translate with a translation API
Today I would like to share about a laravel package that I wrote recently. That package is to translate languages easily using a translation API. I had to use a translation api in my project. Then I wanted to write short code for translation feature and reuse it for future. So I created this package locally.
Methods that can be used
After creating Translation Object, you can use the following methods.
$obj = new Translate();Translation
$translated_text = $obj->translate('Hello World", 'EN', 'JA');
echo $translated_text;
Getting supported languages
$languages = $obj->languages();
foreach($languages as $lang){
echo $lang['language']."-".$lang['name'].'<br>';
}
Getting supported source–languages
$source_languages = $obj->languages('source');
foreach($source_languages as $lang){
echo $lang['language']."-".$lang['name'].'<br>';
}
Getting supported target–languages
$target_languages = $obj->languages('target');
foreach($target_languages as $lang){
echo $lang['language']."-".$lang['name'].'<br>';
}
You can monitor your usage of translation API
$usage= $obj->usage();
echo $usage['character_count'].' characters have been used. Maximum number of characters that can be translated in the current billing period are '.$usage['character_limit'];
You can setup a timeout in requesting api
$obj->setTimeout(10);
Hope you enjoyed that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2021年10月26日 10:00:00