技術情報
- 2023年06月13日
- 技術情報
Python Decorators
Today, I would like to share about Python decorators which simplify the code with powerful function enhancements. Python decorators are a powerful feature that allows developers to modify or enhance the behavior of functions or classes without directly modifying their source code. Decorators provide a clean and concise way to add functionality to existing code, making it easier to manage and reuse.
What are Decorators?
Decorators are functions that take another function as input and extend its functionality. They wrap the original function with additional code, allowing for actions like logging, authentication, and more, to be applied to multiple functions in a consistent and reusable manner.
Example 1: Logging Decorator
Let’s consider a simple example of a logging decorator. The decorator adds logging statements before and after the execution of a function:
def logger(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(f"Calling function: {func.__name__}")
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
print(f"Function {func.__name__} executed")
return result
return wrapper
@logger
def add(a, b):
return a + b
# Using the decorated function
result = add(3, 5)
print(result) # Output: 8In this example, the `logger` function is a decorator that takes the function `add` as input. It defines an inner function `wrapper`, which performs the logging operations and calls the original function. The decorator then returns the `wrapper` function, which replaces the original `add` function.
Example 2: Authorization Decorator
Decorators can also be used for implementing authorization checks. Let’s see an example:
def authenticate(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
if check_authentication():
return func(*args, **kwargs)
else:
raise Exception("Unauthorized access!")
return wrapper
@authenticate
def sensitive_operation():
# Perform sensitive operation here
pass
# Using the decorated function
sensitive_operation()In this example, the `authenticate` decorator checks if the user is authenticated before executing the `sensitive_operation` function. If the user is authenticated, the function is executed; otherwise, an exception is raised.
Conclusion
Python decorators provide a powerful and flexible way to modify the behavior of functions or classes without modifying their original code. They enable code reuse, separation of concerns, and cleaner code organization. By using decorators, developers can enhance their programs with additional features, such as logging, authentication, caching, and more, with minimal effort and maximum efficiency.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2023年06月13日 10:00:00
- 2023年06月06日
- 技術情報
TypeScript and its usefulness
In web development, JavaScript has long been the go-to language for creating interactive and dynamic web applications. However, as projects grow in complexity, the need for better tooling and code organization arises. This is where TypeScript steps in, offering developers a more structured and reliable way to build JavaScript applications. Today, we will explore what TypeScript is and why it is useful.
What is TypeScript?
TypeScript is an open-source programming language developed and maintained by Microsoft. It is a superset of JavaScript, meaning that any valid JavaScript code is also valid TypeScript code. However, TypeScript adds additional features on top of JavaScript, primarily static typing.
Static Typing
Static typing is one of the key features that sets TypeScript apart from JavaScript. With TypeScript, developers can specify the types of variables, function parameters, and return values. This helps catch errors and bugs at compile-time, before the code is executed. By explicitly defining types, developers can achieve better code quality, improved maintainability, and enhanced tooling support.
Code Readability and Maintainability
TypeScript promotes code readability and maintainability by providing a clear structure to the codebase. With the help of static types, developers can easily understand the intended usage of variables, functions, and classes. Additionally, TypeScript supports features such as classes, interfaces, and modules, which allow for better code organization and reusability. This leads to cleaner and more maintainable code, making it easier for developers to collaborate and maintain the project over time.
Enhanced Tooling and IDE Support
TypeScript comes with excellent tooling and IDE support, thanks to its strong type system. IDEs like Visual Studio Code provide intelligent code completion, type checking, and error detection, which significantly enhance the development experience. The TypeScript compiler itself helps catch common errors and offers helpful suggestions during development. These tools enable developers to write code faster and with fewer mistakes, boosting productivity and reducing debugging time.
Integration with Existing JavaScript Codebase
One of the biggest advantages of TypeScript is its seamless integration with existing JavaScript projects. Since TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript, developers can gradually introduce TypeScript into their codebase without the need for a complete rewrite. TypeScript allows for incremental adoption, enabling developers to start reaping the benefits of static typing in their existing projects right away.
Conclusion
TypeScript offers significant advantages for JavaScript developers, enhancing code quality, readability, and maintainability. With static typing, better tooling support, and seamless integration with existing JavaScript codebases, TypeScript empowers developers to build robust and scalable applications. By adopting TypeScript, developers can mitigate common pitfalls, catch errors early, and ultimately deliver high-quality software.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2023年06月06日 10:00:00
- 2023年06月05日
- 技術情報
New Google Play Books feature to help kids to read
Google Play Books has added new features aimed at helping new readers improve their vocabulary and comprehension independently. Google announced today that a new feature called “Reading Practice” is now available in the Google Play Books Android app and Google Kids Space in the US. This tool is intended for children from his 0 years old to her 8 years old.
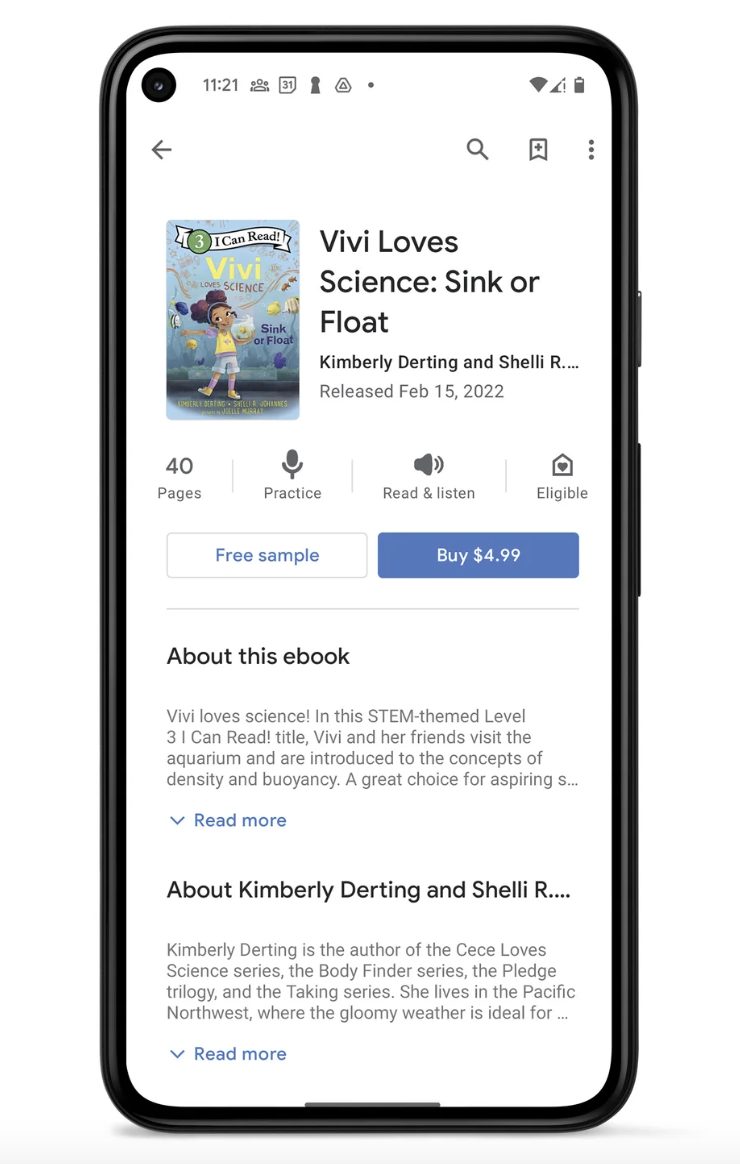
Reading Practice helps early readers track where they are reading by highlighting text as it is read aloud. If your readers don’t know how to pronounce a word, they can touch it to hear how it sounds. If you need more help and want to pronounce a word, you can listen to the word broken down by syllables.

With this feature, you can listen to complete sentences and get child-friendly word definitions, giving your child more context about the story you’re reading. Readers can also tap any word to update their position in the book and start tracking from there. At the bottom of the page, you have the option to practice words that the reader has missed or mispronounced.
You can check out the original blog from google here.
Yuuma
yuuma at 2023年06月05日 10:00:00
- 2023年05月30日
- 技術情報
Different Ways to Make HTTP Requests in JavaScript
When it comes to web development, making HTTP requests is a fundamental aspect of building interactive and dynamic applications. JavaScript provides several techniques and libraries that simplify the process of sending HTTP requests and receiving responses. Today, I will show different approaches to making HTTP requests in JavaScript, highlighting their unique features and use cases.
1. XMLHttpRequest Object
The XMLHttpRequest (XHR) object is a built-in feature of JavaScript that enables asynchronous communication with a server. It has been the traditional method for making HTTP requests in JavaScript. XHR offers flexibility and control over the request, allowing you to handle events, set headers, and handle different response types. However, it requires more manual handling and can be verbose in code.
Example
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', 'https://api.example.com/data', true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (xhr.readyState === 4 && xhr.status === 200) {
var response = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
console.log(response);
}
};
xhr.send();2. Fetch API
Introduced in modern browsers, the Fetch API offers a more modern and straightforward approach to making HTTP requests. It provides a promise-based interface and a simpler syntax compared to XHR, making it easier to use and read. Fetch supports various request methods, handles response types, and provides better error handling.
Example
fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));3. Axios
Axios is a popular JavaScript library for making HTTP requests, commonly used in both browser and Node.js environments. It encapsulates XHR and provides a simple and intuitive API, enhancing code readability and maintainability. Axios supports promises and offers features like request cancellation, interceptors, and automatic JSON parsing.
Example
axios.get('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => console.log(response.data))
.catch(error => console.error(error));4. jQuery AJAX
jQuery, a widely-used JavaScript library, provides an AJAX method for making asynchronous HTTP requests. It simplifies the process with a concise syntax and cross-browser compatibility. However, note that using jQuery only for AJAX requests might not be necessary if you’re not using other jQuery features.
Example
$.ajax({
url: 'https://api.example.com/data',
method: 'GET',
success: function(response) {
console.log(response);
},
error: function(error) {
console.error(error);
}
});Conclusion
Making HTTP requests in JavaScript is crucial for interacting with servers and fetching data in modern web applications. Whether you opt for the traditional XMLHttpRequest object, the modern Fetch API, the versatile Axios library, or the simplicity of jQuery AJAX, each approach has its strengths and fits different use cases. You can choose the method that aligns with your project’s requirements.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2023年05月30日 10:00:00
- 2023年05月23日
- 技術情報
Load Balancing to keep the systems running smoothly
Nowadays, websites and applications need to handle high volumes of traffic to ensure smooth user experiences. But what happens when the load becomes too much for a single server to handle? This is where load balancing comes into play. Load balancing is like having a team of servers working together to share the workload, ensuring that everything runs smoothly. Today, I will explain about load balancing and its importance in keeping your systems up and running.
What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing is the process of distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers, also known as a server cluster or server farm. Instead of relying on a single server to handle all the requests, load balancers evenly distribute the traffic among the servers, optimizing their performance and ensuring high availability.
How Does Load Balancing Work?
Load balancers act as the traffic managers for your server cluster. When a user sends a request to access your website or application, it first reaches the load balancer. The load balancer then analyzes the incoming traffic and distributes it across the available servers based on predefined algorithms or configurations.
Most used types of Load Balancing Algorithms
1. Round Robin: This algorithm distributes traffic equally among the servers in a sequential manner.
2. Least Connections: The load balancer directs incoming traffic to the server with the fewest active connections, optimizing resource utilization.
3. IP Hash: Traffic is distributed based on the source IP address, ensuring that requests from the same IP always reach the same server, which can be useful for session persistence.
Benefits of Load Balancing
1. Scalability: Load balancing allows you to easily scale your infrastructure by adding more servers to handle increased traffic without disrupting user experiences.
2. High Availability: By distributing traffic across multiple servers, load balancing helps eliminate single points of failure, ensuring that your systems remain operational even if one server fails.
3. Improved Performance: Load balancing optimizes resource utilization and prevents overloading of servers, resulting in faster response times and improved performance for users.
4. Flexibility: Load balancers can intelligently route traffic based on various factors like server health, geographic location, or specific content requirements, giving you the flexibility to meet specific needs.
Conclusion
Load balancing is a crucial component of modern web infrastructure, ensuring that your websites and applications can handle high volumes of traffic while maintaining optimal performance and availability. By evenly distributing the workload across multiple servers, load balancers help prevent bottlenecks and improve overall system efficiency. Implementing load balancing in your infrastructure is a smart decision that can enhance user experiences, increase scalability, and keep your systems running smoothly even during peak times.
This is all for now. Hope you enjoy that.
By Asahi
waithaw at 2023年05月23日 10:00:00